app网站建设教程视频教程,h5 和手机网站,互联网公司名称大全,ip怎么做网站简介
文章详细介绍了构建自进化AI智能体的训练架构#xff0c;涵盖强化学习算法、策略建模和分布式训练等关键技术。通过定义训练基础、构建分布式流水线、添加强化学习层、设计动态奖励系统和多阶段训练循环#xff0c;实现智能体在动态环境中的学习和适应。文章提供了多智…简介文章详细介绍了构建自进化AI智能体的训练架构涵盖强化学习算法、策略建模和分布式训练等关键技术。通过定义训练基础、构建分布式流水线、添加强化学习层、设计动态奖励系统和多阶段训练循环实现智能体在动态环境中的学习和适应。文章提供了多智能体科学系统的实现案例展示了如何通过实时反馈和奖励机制使智能体不断改进和进化。深入探讨强化学习算法、策略建模、分布式训练等智能体系统Agentic systems无论是为工具使用还是为推理而设计都依赖于提示词来指导其行动。但提示词是静态的它们仅提供步骤无法自我改进。真正的智能体训练源于系统在动态环境中学习、适应和协作的方式。在智能体架构中每个子智能体都有不同的目标这意味着单一算法无法适用于所有智能体。为了使这些系统更有效我们需要一个集成了推理、奖励和实时反馈的完整训练架构。一个典型的智能体系统训练架构涉及多个相互关联的组件包括智能体训练架构由 Fareed Khan 创建首先我们定义训练基础通过设置环境、初始化智能体状态并将其目标与系统目标对齐。接下来我们构建分布式训练流水线让多个智能体可以并行交互、学习并通过共享内存或日志交换知识。我们添加强化学习层该层使用 SFT监督微调等算法对初学者进行训练使用 PPO 进行高级优化以及使用上下文老虎机进行自适应决策从而实现自我提升。我们连接可观测性和监控工具如追踪钩子和日志适配器以实时捕获每个交互和学习步骤。我们设计一个动态奖励系统使智能体能根据其性能、对齐度和对整体任务的贡献接收反馈。我们创建一个多阶段训练循环智能体在其中经历不同阶段从监督微调到完全基于强化学习的适应。最后我们评估和完善该架构通过分析所有智能体角色的奖励曲线、性能指标和定性行为。在本博客中我们将……构建一个完整的多智能体系统结合推理、协作和强化学习Reinforcement Learning, RL使智能体能够通过实时反馈和奖励进行适应和改进。目录• 为研究实验室奠定基础• 配置研究环境• 获取医学知识库• 定义分层 AgentState• 构建科学工具系统• 设计我们的科学家社群 (LangGraph)• 构建多智能体科学系统• 具有 ReAct 逻辑的高级 StateGraph• 具有复杂奖励系统的 LitAgent• 创建 MedicalResearchAgent• 多方面奖励系统• 创建基于强化学习的训练架构• 创建分布式神经系统• 使用 LLMProxy 作为多模型中心实现可观测性• 创建数据流水线 HierarchicalTraceAdapter• 使用 WandbLoggingHook 进行实时监控• 实现三种强化学习算法• 使用 SFT 算法训练初级研究员• 使用 PPO 算法优化高级研究员• 用于主管策略的上下文老虎机• 构建基于三个阶段的训练循环• 性能评估与分析• 使用奖励曲线和性能指标进行验证• 定性分析• 使用多指标评估进行综合评估• 单次运行的 LangSmith 追踪• 我们的强化学习训练逻辑如何工作为研究实验室奠定基础当我们开始构建一个生产级production-gradeAI 系统时我们不会立即从算法入手而是首先为整个系统奠定坚实的基础。这个初始设置至关重要我们在此做出的每一个选择从安装的库到获取的数据都将决定我们最终训练出的智能体的可靠性和可复现性。因此在本节中我们将执行以下操作• 我们将安装分层训练设置所需的所有核心库和专门依赖项。• 然后我们将配置 API 密钥避免硬编码值并连接我们的 LangSmith 项目以实现可观测性。• 配置完成后我们将下载并处理 PubMedQA 数据集为我们的智能体构建一个高质量的语料库。• 我们还将设计中央的AgentState这是实现协作和推理的共享内存。• 然后我们将为智能体配备必要的工具如模拟数据库、实时网络搜索等以进行外部交互。配置研究环境首先我们需要设置我们的 Python 环境。我们将使用uv而非简单的pip install因为它是一个快速而现代的包管理器能确保我们的环境既能快速搭建又具有高度可复现性适合生产环境。我们还将为agent-lightning安装特定的verl扩展用于我们的 PPO 算法以及apo(Asynchronous Policy Optimization) 和unsloth用于高效的 SFT这些对于我们高级的分层训练策略至关重要。print(Updating and installing system packages...)# We first update the systems package list and install uv and graphviz.# graphviz is a system dependency required by LangGraph to visualize our agentic workflows.!apt-get update -qq apt-get install -y -qq uv graphvizprint(\nInstalling packages...\n)# Here, we use uv to install our Python dependencies.# We install the [verl,apo] extras for Agent-Lightning to get the necessary components for PPO and other advanced RL algorithms.# [unsloth[pt231]] provides a highly optimized framework for Supervised Fine-Tuning, which well use for our Junior Researchers.!uv pip install -q -U langchainlanggraphlangchain_openaitavily-pythonagentlightning[verl,apo]unsloth[pt231]pandasscikit-learnrichwandbdatasetspyarrowprint(Successfully installed all required packages.)让我们开始安装过程……#### OUTPUT ####Updating and installing system packages......Installing packages...Resolved 178 packages in 3.12s... agentlightning0.2.2 langchain0.2.5 langgraph0.1.5 unsloth2024.5 verl0.6.0...Successfully installed all required packages.通过安装graphviz我们启用了LangGraph的可视化功能这对于后续调试我们复杂的智能体社群将非常有价值。更重要的是安装带有verl和unsloth扩展的agentlightning为我们提供了分层策略所需的高性能特定训练后端。我们现在有了一个稳定而完整的基础。现在可以开始预处理训练数据了。获取医学知识库每个机器学习系统都需要训练数据或者至少需要一些初始观察才能开始自学习。我们的智能体不能孤立地进行推理它们需要访问丰富的、特定领域的信息。预处理知识库数据由 Fareed Khan 创建一个静态的、硬编码的事实列表过于简单。为了构建一个现实且具有挑战性的研究环境我们将从 PubMedQA 数据集 中提取我们的知识库特别是利用其标记子集 pqa_l。它包含真实的生物医学问题、提供必要上下文的原始科学摘要以及由人类专家确定的最终**‘是/否/可能’**答案。这种结构不仅为我们的智能体提供了一个丰富的信息来源进行搜索还提供了一个基准真相ground truth我们可以用它来为我们的强化学习循环计算奖励。首先让我们定义一个简单的TypedDict来结构化每个任务。这能确保我们的数据在整个流水线中保持干净和一致。from typing import List, TypedDict# A TypedDict provides a clean, structured way to represent each research task.# This makes our code more readable and less prone to errors from using plain dictionaries.class ResearchTask(TypedDict): id: str # The unique PubMed ID for the article goal: str # The research question our agent must investigate context: str # The full scientific abstract providing the necessary evidence expected_decision: str # The ground truth answer (yes, no, or maybe)我们基本上是使用TypedDict创建了一个ResearchTask蓝图。这不仅仅是一个普通的字典它是一个强制执行特定数据结构的契约。现在每个任务都将一致地拥有id、goal、context和expected_decision。这种严格的类型定义是一种最佳实践可以防止后续的错误确保我们系统的每个组件都确切地知道期望什么样的数据。定义好数据结构后我们现在可以编写一个函数来从 Hugging Face Hub 下载数据集将其处理成我们的ResearchTask格式并分割成训练集和验证集。一个独立的验证集对于客观评估我们智能体在训练后的性能至关重要。from datasets import load_datasetimport pandas as pddefload_and_prepare_dataset() - tuple[List[ResearchTask], List[ResearchTask]]: Downloads, processes, and splits the PubMedQA dataset into training and validation sets. print(Downloading and preparing PubMedQA dataset...) # Load the pqa_l (labeled) subset of the PubMedQA dataset. dataset load_dataset(pubmed_qa, pqa_l, trust_remote_codeTrue) # Convert the training split to a pandas DataFrame for easier manipulation. df dataset[train].to_pandas() # This list will hold our structured ResearchTask objects. research_tasks [] # Iterate through each row of the DataFrame to create our tasks. for _, row in df.iterrows(): # The CONTEXTS field is a list of strings; we join them into a single block of text. context_str .join(row[CONTEXTS]) # Create a ResearchTask dictionary with the cleaned and structured data. task ResearchTask( idstr(row[PUBMED_ID]), goalrow[QUESTION], contextcontext_str, expected_decisionrow[final_decision] ) research_tasks.append(task) # We perform a simple 80/20 split for our training and validation sets. train_size int(0.8 * len(research_tasks)) train_set research_tasks[:train_size] val_set research_tasks[train_size:] print(fDataset downloaded and processed. Total samples: {len(research_tasks)}) print(fTrain dataset size: {len(train_set)} | Validation dataset size: {len(val_set)}) return train_set, val_set# Lets execute the function.train_dataset, val_dataset load_and_prepare_dataset()我们刚刚编写的load_and_prepare_dataset函数是我们的数据摄取流水线。它自动化了获取知识库的整个过程连接到 Hugging Face Hub下载原始数据最重要的是将其从通用的 DataFrame 转换为我们自定义的ResearchTask对象的干净列表。80/20 的划分是标准的机器学习实践它为我们提供了一个庞大的数据集用于训练train_set以及一个独立的、未见过的数据集val_set用于后续测试我们的智能体知识泛化的程度。数据加载后检查一个样本总是一个好习惯。这有助于我们确认解析逻辑是否正确并让我们对智能体将面临的挑战类型有一个直观感受。我们将编写一个小工具函数用一个清晰、易读的表格来显示几个例子。from rich.console import Consolefrom rich.table import Tableconsole Console()defdisplay_dataset_sample(dataset: List[ResearchTask], sample_size5): Displays a sample of the dataset in a rich, formatted table. # Create a table for display using the rich library for better readability. table Table(titlePubMedQA Research Goals Dataset (Sample)) table.add_column(ID, stylecyan) table.add_column(Research Goal (Question), stylemagenta) table.add_column(Expected Decision, stylegreen) # Populate the table with the first few items from the dataset. for item in dataset[:sample_size]: table.add_row(item[id], item[goal], item[expected_decision]) console.print(table)display_dataset_sample(train_dataset)这个display_dataset_sample函数是我们的健全性检查。通过使用rich库创建一个格式化的表格我们可以快速清晰地验证加载数据的结构。这比仅仅打印原始字典要有效得多。以这种方式展示数据确认了我们的load_and_prepare_dataset函数正确地为每个任务提取了ID、goal和expected_decision。让我们看一下我们刚刚编写的上述函数的输出。#### OUTPUT ####Downloading and preparing PubMedQA dataset...Dataset downloaded and processed. Total samples: 1000Train dataset size: 800 | Validation dataset size: 200--- Sample 0 ---ID: 11843333Goal: Do all cases of ulcerative colitis in childhood need colectomy?Expected Decision: yesContext (first 200 chars): A retrospective review of 135 children with ulcerative colitis was performed to determin ...我们已经将原始的 PubMedQA 数据转换成了一个干净、结构化的ResearchTask对象列表并分成了训练集和验证集。此表中的每一行都代表一个完整的研究挑战我们可以将其输入到智能体的rollout方法中。Research Goal将作为初始提示而Expected Decision将作为计算最终奖励信号的基准真相。我们的智能体现在有了一个世界级的、现实的知识库可供学习。一直在更新更多的大模型学习和面试资料已经上传带到CSDN的官方了有需要的朋友可以扫描下方二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】定义分层 AgentState在获取并结构化数据之后我们现在需要设计我们智能体社群的**“神经系统”。这是共享内存或称状态**它将使我们多样化的智能体群体能够协作、传递信息并在彼此的工作基础上进行构建。在LangGraph中这个共享内存由一个中央状态对象管理。对于像我们这样复杂的系统一个简单的字典会过于脆弱。因此我们将使用 Python 的TypedDict构建一个嵌套的、分层的AgentState。AgentState由 Fareed Khan 创建这种方法为我们智能体的整个认知过程提供了一个机器可读的蓝图。我们状态中的每个字段都将代表研究工作流的一个不同阶段从初级研究员生成的初始假设到最终经过同行评审的方案。以下是我们将要做的•定义子状态我们将为特定产物如JuniorResearch、Protocol和ReviewDecision创建更小的TypedDict类。•构建主状态将这些子状态组装到主AgentState中它将保存单次研究运行的所有信息。•启用 ReAct 逻辑添加一个sender字段这是一个关键组件允许我们构建健壮的 ReAct 风格循环其中工具结果被路由回正确的智能体。首先让我们为初级研究员的输出定义数据结构。这确保了他们生成的每个假设都具有一致的格式。from typing import List, TypedDict, Literalfrom langchain_core.messages import BaseMessage# This defines the structure for a single hypothesis from a Junior Researcher.# It captures the core idea, the evidence found, and which agent proposed it.class JuniorResearch(TypedDict): hypothesis: str supporting_papers: List[str] agent_name: str # To track which junior researcher proposed it我们基本上是为**“假设提交”**创建了一个蓝图。JuniorResearch类使用TypedDict来强制每个提交都必须包含一个hypothesis字符串、一个supporting_papers列表和agent_name。这种结构对主管智能体非常重要因为它保证了它将收到一组格式一致的提案每个提案都有明确的出处。接下来我们将为实验方案定义结构。这是我们高级研究员的主要输出需要详细且可操作。# This defines the structure for the final experimental protocol.# Its a detailed, actionable plan.class Protocol(TypedDict): title: str steps: List[str] safety_concerns: str budget_usd: floatProtocol类规范了科学实验的关键组成部分。通过要求title、steps列表、safety_concerns部分和budget_usd我们正在指导我们的高级研究员智能体思考其提案的实际细节。这种结构化的输出远比一个简单的文本块更有价值并将成为我们最终奖励计算的基础。现在让我们为评审委员会的反馈创建结构。这对于我们的修订循环至关重要因为它需要既清晰又机器可读。# This defines the structured feedback from our review agents.# It forces a clear decision, a severity level, and constructive feedback.class ReviewDecision(TypedDict): decision: Literal[APPROVE, REVISE] critique_severity: Literal[CRITICAL, MAJOR, MINOR] feedback: str在这里我们设计了ReviewDecision类来捕捉一份评论的细致输出。Literal的使用是一个关键的工程设计它迫使评审智能体做出一个离散的选择APPROVE或REVISE。对他们反馈的严重性进行分类CRITICAL、MAJOR或MINOR。通过这种方式我们允许我们的LangGraph路由器决定是应该将方案发回进行重大重写还是小幅调整。最后我们可以将这些较小的结构组装到我们的主AgentState中。这将是追踪研究运行期间发生的所有事情的单一、全面的对象。from typing import Annotated# This is the master state dictionary that will be passed between all nodes in our LangGraph.classAgentState(TypedDict): # The messages field accumulates the conversation history. # The lambda x, y: x y tells LangGraph how to merge this field: by appending new messages. messages: Annotated[List[BaseMessage], lambda x, y: x y] research_goal: str# The initial high-level goal from our dataset. sender: str # Crucial for ReAct: tracks which agent last acted, so tool results can be sent back to it. turn_count: int # A counter to prevent infinite loops in our graph. # Junior Researcher Teams output (accumulates from parallel runs) initial_hypotheses: List[JuniorResearch] # Supervisors choice selected_hypothesis: JuniorResearch supervisor_justification: str # Senior Researcher Teams output refined_hypothesis: str experimental_protocol: Protocol # Review Boards output peer_review: ReviewDecision safety_review: ReviewDecision # Principal Investigators final decision final_protocol: Protocol final_decision: Literal[GO, NO-GO] final_rationale: str # The final evaluation score from our reward function final_evaluation: dict我们现在已经成功定义了我们智能体社群的整个认知架构。信息的流动是清晰的生成initial_hypotheses选择其中一个作为selected_hypothesis将其完善为experimental_protocol经过peer_review和safety_review最终得出final_decision。sender字段尤其重要。在一个 ReAct推理-行动Reason-Act循环中一个智能体决定使用一个工具。工具运行后系统需要知道将结果返回给哪个智能体。通过在每次智能体行动时更新sender字段我们创建了一个明确的返回地址从而实现了这种复杂的、来回往复的推理模式。有了这个状态定义我们的图现在有了一个坚实的内存结构。构建科学工具系统我们的智能体现在有了复杂的内存AgentState但要进行研究它们需要访问外部世界或者用更技术的术语来说是外部知识库external knowledgebase。一个没有工具的智能体只是一个对话者一个拥有工具的智能体则成为一个能够收集实时、特定领域信息的强大行动者。科学工具由 Fareed Khan 创建在本节中我们将为我们的智能体社群构建一个ScientificToolkit。这个工具包将提供一套专门的函数我们的智能体可以调用这些函数来执行基本的研究任务。以下是我们将要做的•集成实时网络搜索我们将使用TavilySearchResults工具让我们的智能体能够搜索 PubMed 和 ClinicalTrials.gov 以获取最新的科学文献。•模拟内部数据库我们将为蛋白质和基因本体论创建模拟数据库以模拟智能体如何查询专有的内部知识库。•使用**tool**装饰器使用 LangChain 的tool装饰器使这些 Python 函数能够被我们由 LLM 驱动的智能体发现和调用。•测试一个工具然后对我们的一个新工具进行快速测试调用以确保一切都已正确连接。首先让我们定义一个类来容纳我们所有的工具。将它们分组在一个类中是组织和状态管理如管理 API 客户端的良好实践。from langchain_core.tools import toolfrom langchain_community.tools.tavily_search import TavilySearchResultsclassScientificToolkit: def__init__(self): # Initialize the Tavily search client, configured to return the top 5 results. self.tavily TavilySearchResults(max_results5) # This is a mock database simulating an internal resource for protein information. self.mock_protein_db { amyloid-beta: A key protein involved in the formation of amyloid plaques in Alzheimers., tau: A protein that forms neurofibrillary tangles inside neurons in Alzheimers., apoe4: A genetic risk factor for Alzheimers disease, affecting lipid metabolism in the brain., trem2: A receptor on microglia that, when mutated, increases Alzheimers risk., glp-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1, a hormone involved in insulin regulation with potential neuroprotective effects. } # This is a second mock database, this time for gene functions. self.mock_go_db { apoe4: A major genetic risk factor for Alzheimers disease, involved in lipid transport and amyloid-beta clearance., trem2: Associated with microglial function, immune response, and phagocytosis of amyloid-beta. }我们现在已经为我们的ScientificToolkit搭建好了基础。让我们快速理解一下……__init__方法初始化了我们的实时网络搜索工具 (Tavily)。设置了两个简单的 Python 字典 (mock_protein_db,mock_go_db) 来模拟内部的专有数据库。这种实时工具和模拟工具的结合是对真实世界企业环境的现实写照在真实环境中智能体需要同时访问公共和私有数据源。现在让我们定义实际的工具方法。每个方法都将是我们希望赋予智能体的特定能力。我们将从 PubMed 搜索工具开始。tool def pubmed_search(self, query: str) - str: Searches PubMed for biomedical literature. Use highly specific keywords related to genes, proteins, and disease mechanisms. console.print(f--- TOOL: PubMed Search, Query: {query} ---) # We prepend site:pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov to the query to restrict the search to PubMed. return self.tavily.invoke(fsite:pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov {query})我们首先定义了我们的第一个工具pubmed_search。来自 LangChain 的tool装饰器为我们简化了工作它自动将这个 Python 函数转换成一个 LLM 能够理解并决定调用的结构化工具。接下来我们将创建一个类似的工具用于搜索临床试验。tool def clinical_trials_search(self, query: str) - str: Searches for information on clinical trials related to specific drugs or therapies. console.print(f--- TOOL: Clinical Trials Search, Query: {query} ---) # This tool is focused on ClinicalTrials.gov to find information about ongoing or completed studies. return self.tavily.invoke(fsite:clinicaltrials.gov {query})这个clinical_trials_search工具是另一个专业化的实时数据工具的例子。通过将搜索限制在clinicaltrials.gov我们为智能体提供了一种专注的方式来查找有关药物开发流程和治疗干预的信息这与通常在 PubMed 摘要中找到的信息类型不同。现在让我们实现与我们的模拟内部数据库交互的工具。tool defprotein_database_lookup(self, protein_name: str) - str: Looks up information about a specific protein in our mock database. console.print(f--- TOOL: Protein DB Lookup, Protein: {protein_name} ---) # This simulates a fast lookup in a proprietary, internal database of protein information. returnself.mock_protein_db.get(protein_name.lower(), Protein not found.) tool defgene_ontology_lookup(self, gene_symbol: str) - str: Looks up the function and pathways associated with a specific gene symbol in the Gene Ontology database. console.print(f--- TOOL: Gene Ontology Lookup, Gene: {gene_symbol.upper()} ---) # This simulates a query to another specialized internal database, this time for gene functions. result self.mock_go_db.get(gene_symbol.lower(), fGene {gene_symbol} not found in ontology database.) console.print(fGene {gene_symbol.upper()} lookup result: {result}) return result这两个函数protein_database_lookup和gene_ontology_lookup展示了如何将智能体与内部或专有数据源集成。尽管在这个演示中我们使用的是简单的字典但在真实系统中这些函数可能包含连接到 SQL 数据库、私有 API 或专业生物信息学库例如医院的私有数据库的逻辑。最后让我们实例化我们的工具包并将所有工具函数整合到一个列表中这样我们就可以方便地将其传递给我们的智能体运行器。# Instantiate our toolkit class.toolkit ScientificToolkit()# Create a list that holds all the tool functions weve defined.all_tools [toolkit.pubmed_search, toolkit.clinical_trials_search, toolkit.protein_database_lookup, toolkit.gene_ontology_lookup]print(Scientific Toolkit with live data tools defined successfully.)# Test the new gene_ontology_lookup tool to confirm its working.toolkit.gene_ontology_lookup.invoke(APOE4)让我们运行这段代码看看我们工具包的输出是什么样的……#### OUTPUT ####Scientific Toolkit with live data tools defined successfully.--- TOOL: Gene Ontology Lookup, Gene: APOE4 ---Gene APOE4 lookup result: A major genetic risk factor for Alzheimers disease, involved in lipid transport and amyloid-beta clearance.我们可以看到输出确认了我们的ScientificToolkit已经成功实例化并且我们的新gene_ontology_lookup工具工作正常。all_tools列表现在是一个完整的、可移植的能力集合我们可以将它绑定到我们的任何一个智能体上。通过这种方式我们正在积极地为我们的智能体系统寻找并集成来自多个来源的信息将它们从简单的推理者转变为活跃的研究者。设计我们的科学家社群 (LangGraph)随着我们的基础组件——安全的环境、数据集、分层的AgentState和强大的ScientificToolkit——都已就位我们现在准备好构建智能体本身了。在这一步我们将从定义数据结构转向工程化将要执行研究的认知实体简单来说我们将构建我们多智能体系统的核心组件。子智能体系统由 Fareed Khan 创建在本节中我们将使用LangGraph来设计和编排我们的多智能体社群。为了模拟真实的工作流程我们将创建一个专家团队每个成员都有特定的角色并由精心选择的开源模型提供支持。以下是我们将要做的•分配角色和模型为我们的每个 AI 科学家定义**“角色”**并根据他们任务的复杂性为他们分配不同的开源模型。•创建智能体运行器创建一个工厂函数该函数接收一个模型、一个提示和一组工具并生成一个可运行的智能体执行器。•构建 StateGraph我们将使用LangGraph将这些智能体连接在一起实现先进的 ReAct 逻辑和一个多层次的修订循环以创建一个健壮的、循环的工作流程。•可视化架构生成我们最终图的工作流程图以获得我们智能体社群认知架构的清晰、直观的图像。构建多智能体科学系统高级智能体设计的一个关键原则是并非所有任务都是平等的。为每项工作都使用一个单一的、巨大的模型是低效且昂贵的。因此我们将策略性地从 Hugging Face Hub 中为我们研究团队内的不同角色分配不同的开源模型。这种**“为合适的任务选择合适的模型”**的方法是构建生产级、成本效益高的智能体系统的基石。多智能体系统由 Fareed Khan 创建我们需要定义 LLM 配置。我们将为初级研究员的创造性头脑风暴使用一个小型、快速的模型为我们将用PPO 微调的高级研究员预留一个更强大模型的占位符并为关键的评审任务使用一个能力很强的混合专家模型mixture-of-experts model。import osfrom langchain_openai import ChatOpenAIfrom langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder# We will use different open-source models for different roles to optimize performance and cost.# The openai_api_base will be dynamically set by the LLMProxy during training,# pointing to a local server (like Ollama or vLLM) instead of OpenAIs API.junior_researcher_llm ChatOpenAI( modelQwen/Qwen2-1.5B-Instruct, # A small, fast model for creative, parallel brainstorming. temperature0.7, openai_api_basehttp://localhost:11434/v1, # Assuming an Ollama server is running locally. openai_api_keyollama)supervisor_llm ChatOpenAI( modelQwen/Qwen2-1.5B-Instruct, # The same small model is sufficient for the structured selection task. temperature0.0, openai_api_basehttp://localhost:11434/v1, openai_api_keyollama)# This is a special placeholder. During training, the VERL algorithm will serve the Llama-3 model# under this logical name via the Agent-Lightning LLMProxy.senior_researcher_llm ChatOpenAI( modelsenior_researcher_llm, # A logical name, not a real model endpoint initially. temperature0.1, openai_api_basehttp://placeholder-will-be-replaced:8000/v1, openai_api_keydummy_key)# For the critical review and final decision stages, we use a more powerful model.review_board_llm ChatOpenAI( modelmistralai/Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct-v0.1, # A powerful Mixture-of-Experts model for nuanced evaluation. temperature0.0, openai_api_basehttp://localhost:11434/v1, openai_api_keyollama)print(Agent personas and open-source LLM configurations are defined.)确保你已经拉取了相应的模型并通过 ollma/vllm 提供服务。我们现在已经定义了我们研究团队的**“硬件”**。通过将Qwen2-1.5B分配给初级角色我们实现了快速、并行和低成本的创意构思。senior_researcher_llm现在被明确地作为一个逻辑占位符这是训练的一个关键概念。Agent-Lightning将拦截对这个模型名称的调用并将它们路由到我们经过 PPO 训练的模型使我们能够在不影响系统其余部分的情况下更新其策略。最后为评审委员会使用强大的Mixtral模型确保了批判和评估步骤以最高水平的审查标准进行。接下来我们需要一个标准化的方法来将模型、系统提示和一组工具组合成一个可运行的智能体。我们将为此创建一个简单的工厂函数。def create_agent_runner(llm, system_prompt, tools): A factory function to create a runnable agent executor. # The prompt consists of a system message, and a placeholder for the conversation history. prompt ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([ (system, system_prompt), MessagesPlaceholder(variable_namemessages), ]) # We bind the tools to the LLM, making them available for the agent to call. return prompt | llm.bind_tools(tools)这个create_agent_runner函数虽然小但在这里却很重要。它规范了我们构建智能体的方式。通过创建一个可重用的**“工厂”**我们确保系统中的每个智能体都以一致的方式构建接收一个定义其角色的特定system_prompt、一个提供其推理能力的llm以及一个它能使用的tools列表。这使得我们的主图构建代码更清晰、更易于管理。最后我们将为我们智能体社群中的每个角色定义具体的系统提示。这些提示是运行在我们 LLM “硬件”上的“软件”引导每个智能体的行为并定义其具体的职责和输出格式。# This is holding the detailed system prompts for each agent role.prompts { Geneticist: You are a geneticist specializing in Alzheimers. Propose a hypothesis related to genetic factors. Use tools to find supporting evidence. Respond with a JSON object: {hypothesis: str, supporting_papers: List[str]}., Pharmacologist: You are a pharmacologist. Propose a drug target hypothesis. Use tools to find clinical trial data. Respond with a JSON object: {hypothesis: str, supporting_papers: List[str]}., Neurologist: You are a clinical neurologist. Propose a systems-level neurobiology hypothesis. Use tools to find papers on brain pathways. Respond with a JSON object: {hypothesis: str, supporting_papers: List[str]}., Supervisor: You are a research supervisor. Review the hypotheses and select the most promising one. Justify your choice based on novelty, feasibility, and impact. Return a JSON object: {selected_hypothesis_index: int, justification: str}., HypothesisRefiner: You are a senior scientist. Deepen the selected hypothesis with more literature review, refining it into a specific, testable statement. Return a JSON object: {refined_hypothesis: str}., ProtocolDesigner: You are a lab manager. Design a detailed, step-by-step experimental protocol to test the refined hypothesis. Be specific about methods, materials, and controls. Return a JSON object: {title: str, steps: List[str], safety_concerns: str, budget_usd: float}., PeerReviewer: You are a critical peer reviewer. Find flaws in the protocol. Be constructive but rigorous. Return a JSON object: {decision: APPROVE|REVISE, critique_severity: CRITICAL|MAJOR|MINOR, feedback: str}., SafetyOfficer: You are a lab safety officer. Review the protocol for safety, regulatory, and ethical concerns. Be thorough. Return a JSON object: {decision: APPROVE|REVISE, critique_severity: CRITICAL|MAJOR|MINOR, feedback: str}., # Note: I corrected a typo from safety_review to feedback for consistency PrincipalInvestigator: You are the Principal Investigator. Synthesize the protocol and reviews into a final document. Make the final GO/NO-GO decision and provide a comprehensive rationale. Return a JSON object: {final_protocol: Protocol, final_decision: GO|NO-GO, final_rationale: str}.}我们现在已经完全定义了我们的 AI 科学家阵容。每个智能体都通过其prompt被赋予了特定的角色通过其llm被赋予了推理引擎并通过tools被赋予了一套能力。这些提示中的一个关键细节是要求以特定的 JSON 对象进行响应。这种结构化输出对于在我们分层的AgentState中可靠地更新工作流从一个智能体传递到下一个智能体至关重要。我们的工作团队现在已经准备好被组装成一个功能齐全的团队。具有 ReAct 逻辑的高级 StateGraph现在我们已经定义了我们的专家智能体团队我们需要建造一个它们可以协作的实验室。这是LangGraph的工作。我们现在将把我们的智能体组装成一个功能性的、循环的工作流创建一个StateGraph来定义我们研究团队每个成员之间的信息和控制流。ReAct 逻辑简化图由 Fareed Khan 创建这不会是一个简单的线性流水线……为了模拟真实的研究过程我们需要实现复杂的逻辑包括用于修订的反馈循环和用于工具使用的健壮机制。在本节中我们将执行以下操作……•构建智能体节点创建一个工厂函数将我们的每个智能体运行器包装成一个LangGraph节点该节点能正确更新我们的AgentState。•实现 ReAct 风格的工具使用定义一个条件边和一个路由器确保在任何智能体使用工具后结果直接返回给同一个智能体进行处理。•设计一个多层次的修订循环设计一个智能的条件边根据我们评审委员会反馈的严重程度来不同地路由工作流从而实现小幅调整和重大反思。•编译和可视化图最后我们将编译完整的StateGraph并生成一个可视化图像以清晰地了解我们智能体的认知架构。首先我们需要一种从我们的智能体运行器创建图节点的方法。我们将创建一个辅助函数它接受智能体的名称及其可运行的执行器并返回一个可以作为节点添加到我们的图中的函数。这个节点函数将处理更新AgentState中的turn_count和sender字段。from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, ENDfrom langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNodefrom langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, BaseMessageimport jsonMAX_TURNS 15# A safeguard to prevent our graph from getting stuck in an infinite loop.# This is a helper function, a factory that creates a node function for a specific agent.defcreate_agent_node(agent_name: str, agent_runner): Creates a LangGraph node function for a given agent runner. defagent_node(state: AgentState) - dict: # Print a console message to trace the graphs execution path. console.print(f--- Node: {agent_name} (Turn {state[turn_count]}) ---) # Increment the turn count as a safety measure. state[turn_count] 1 # Invoke the agent runner with the current state. result agent_runner.invoke(state) # We need to handle the structured JSON output from our review agents specifically. if agent_name in [PeerReviewer, SafetyOfficer]: try: # The agents output is a JSON string in the content of the AIMessage. content json.loads(result.content) # We update the correct field in our AgentState based on which reviewer ran. if agent_name PeerReviewer: state[peer_review] content else: state[safety_review] content # The key here was safety_review, not feedback. except (json.JSONDecodeError, TypeError): # If parsing fails, we log an error but dont crash the graph. console.print(f[bold red]Error parsing JSON from {agent_name}: {result.content}[/bold red]) # We update the messages list and crucially, set the sender field for ReAct routing. return {messages: [result], sender: agent_name} return agent_nodecreate_agent_node函数是我们系统中每个智能体的标准化包装器。它确保每次智能体运行时我们都会记录其活动增加我们的安全计数器turn_count最重要的是更新状态中的sender字段。这最后一步是我们 ReAct 逻辑的关键。它留下了一个“面包屑”这样我们的图就知道刚才谁行动了。对评审智能体的特殊处理确保了它们结构化的 JSON 反馈被正确解析并放入我们AgentState中相应的字段peer_review和safety_review。现在让我们为我们的 ReAct 循环定义条件逻辑。这个函数将检查状态中的最后一条消息。如果它包含工具调用它将把图导向ToolNode。否则它表示该智能体此步骤的推理已完成。def tools_condition(state: AgentState) - str: A conditional edge that checks for tool calls and the turn count. # Examine the most recent message in the state. last_message state[messages][-1] # If the message has no tool calls, the agents turn is done. ifnothasattr(last_message, tool_calls) ornot last_message.tool_calls: returnend # If weve exceeded our maximum number of turns, we also end to prevent loops. if state[turn_count] MAX_TURNS: console.print([bold yellow]Max turns reached. Ending graph.[/bold yellow]) returnend # Otherwise, there are tools to be executed. return toolstools_condition函数是我们 ReAct 循环的决策者。它在每个智能体回合后充当看门人。它的逻辑简单而强大它检查最后一条消息并查找是否存在tool_calls。如果找到它返回字符串tools向LangGraph发出信号将状态路由到我们的工具执行节点。如果没有工具调用或者达到了我们的安全MAX_TURNS限制它返回end允许工作流继续进行。接下来我们需要一个在工具执行之后指导工作流程的路由器。这就是我们的sender字段变得至关重要的地方。# This router function will route the workflow back to the agent that originally called the tool.def route_after_tools(state: AgentState) - str: A router that sends the workflow back to the agent that initiated the tool call. # Get the name of the last agent that acted from the sender field in the state. sender state.get(sender) console.print(f--- Routing back to: {sender} after tool execution ---) if not sender: # If for some reason the sender is not set, we end the graph as a fallback. return END # The returned string must match the name of a node in our graph. return sender这个route_after_tools函数是我们 ReAct 实现的后半部分。它是一个条件边简单地从AgentState中读取由我们的create_agent_node函数留下的sender值并返回它。LangGraph随后将使用这个字符串来路由状态现在状态中包含了工具的输出直接返回给请求它的智能体。这使得智能体能够看到其行动的结果并继续其推理过程。现在是我们最重要的路由逻辑部分即评审阶段之后的多层次修订循环。def route_after_review(state: AgentState) - Literal[PrincipalInvestigator, HypothesisRefiner, ProtocolDesigner]: An intelligent router that determines the next step based on the severity of review feedback. peer_review state.get(peer_review, {}) safety_review state.get(safety_review, {}) # Extract the decision and severity from both reviews, with safe defaults. peer_severity peer_review.get(critique_severity, MINOR) safety_severity safety_review.get(critique_severity, MINOR) # If our safety counter is maxed out, we must proceed to the PI, regardless of feedback. if state[turn_count] MAX_TURNS: console.print([bold yellow]Max turns reached during review. Proceeding to PI.[/bold yellow]) returnPrincipalInvestigator # If EITHER review has a CRITICAL severity, the fundamental hypothesis is flawed. # We route all the way back to the HypothesisRefiner for a major rethink. if peer_severity CRITICALor safety_severity CRITICAL: console.print(--- Review requires CRITICAL revision, routing back to HypothesisRefiner. ---) state[messages].append(HumanMessage(contentCritical feedback received. The core hypothesis needs rethinking.)) returnHypothesisRefiner # If EITHER review has a MAJOR severity (but no critical ones), the protocol itself is flawed. # We route back to the ProtocolDesigner for a significant revision. if peer_severity MAJORor safety_severity MAJOR: console.print(--- Review requires MAJOR revision, routing back to ProtocolDesigner. ---) state[messages].append(HumanMessage(contentMajor feedback received. The protocol needs significant revision.)) returnProtocolDesigner # If there are only MINOR revisions or everything is approved, the protocol is fundamentally sound. # We can proceed to the PrincipalInvestigator for the final decision. console.print(--- Reviews complete, routing to PrincipalInvestigator. ---) return PrincipalInvestigator这个函数是我们迭代优化过程中最重要的组件。它检查AgentState中来自peer_review和safety_review的critique_severity。这使它能够做出一个细致的、分层的路由决策**关键Critical**反馈会触发一个循环一直回到高级研究阶段的开始HypothesisRefiner。**重大Major反馈会触发一个较小的循环回到ProtocolDesigner而次要Minor**或已批准的评审则允许流程向前推进。这种多层次的反馈循环是一个强大的模式模仿了现实世界中项目是如何被修订的。最后我们可以将所有这些部分整合到一个构建器函数中该函数构造并编译我们完整的StateGraph。def build_graph() - StateGraph: workflow StateGraph(AgentState) # Instantiate all our agent runners using the factory function. agent_runners { Geneticist: create_agent_runner(junior_researcher_llm, prompts[Geneticist], all_tools), Pharmacologist: create_agent_runner(junior_researcher_llm, prompts[Pharmacologist], all_tools), Neurologist: create_agent_runner(junior_researcher_llm, prompts[Neurologist], all_tools), Supervisor: create_agent_runner(supervisor_llm, prompts[Supervisor], []), HypothesisRefiner: create_agent_runner(senior_researcher_llm, prompts[HypothesisRefiner], all_tools), ProtocolDesigner: create_agent_runner(senior_researcher_llm, prompts[ProtocolDesigner], all_tools), PeerReviewer: create_agent_runner(review_board_llm, prompts[PeerReviewer], []), SafetyOfficer: create_agent_runner(review_board_llm, prompts[SafetyOfficer], []), PrincipalInvestigator: create_agent_runner(review_board_llm, prompts[PrincipalInvestigator], []) } # Add all the agent nodes and the single tool execution node to the graph. for name, runner in agent_runners.items(): workflow.add_node(name, create_agent_node(name, runner)) workflow.add_node(execute_tools, ToolNode(all_tools)) # ---- Define the graphs control flow using edges ---- # The graph starts by running the three Junior Researchers in parallel. workflow.add_edge(START, Geneticist) workflow.add_edge(START, Pharmacologist) workflow.add_edge(START, Neurologist) # For each agent that can use tools, we add the ReAct conditional edge. for agent_name in [Geneticist, Pharmacologist, Neurologist, HypothesisRefiner, ProtocolDesigner]: # After the agent runs, check for tool calls. workflow.add_conditional_edges( agent_name, tools_condition, { tools: execute_tools, # If tools are called, go to the tool node. end: Supervisorif agent_name in [Geneticist, Pharmacologist, Neurologist] elseProtocolDesignerif agent_name HypothesisRefinerelsePeerReviewer# If no tools, proceed to the next logical step. } ) # After tools are executed, route back to the agent that called them. workflow.add_conditional_edges(execute_tools, route_after_tools) # Define the main linear flow of the research pipeline. workflow.add_edge(Supervisor, HypothesisRefiner) workflow.add_edge(PeerReviewer, SafetyOfficer) # After the SafetyOfficer, use our intelligent review router. workflow.add_conditional_edges(SafetyOfficer, route_after_review) # The PrincipalInvestigator is the final step before the graph ends. workflow.add_edge(PrincipalInvestigator, END) return workflow# Build the graph and compile it into a runnable object.research_graph_builder build_graph()research_graph research_graph_builder.compile()print(LangGraph StateGraph builder is defined and compiled.)# We can also visualize our compiled graph to see the final architecture.try: from IPython.display import Image, display png_image research_graph.get_graph().draw_png() display(Image(png_image))except Exception as e: print(fCould not visualize graph: {e}. Please ensure pygraphviz and graphviz are installed.) 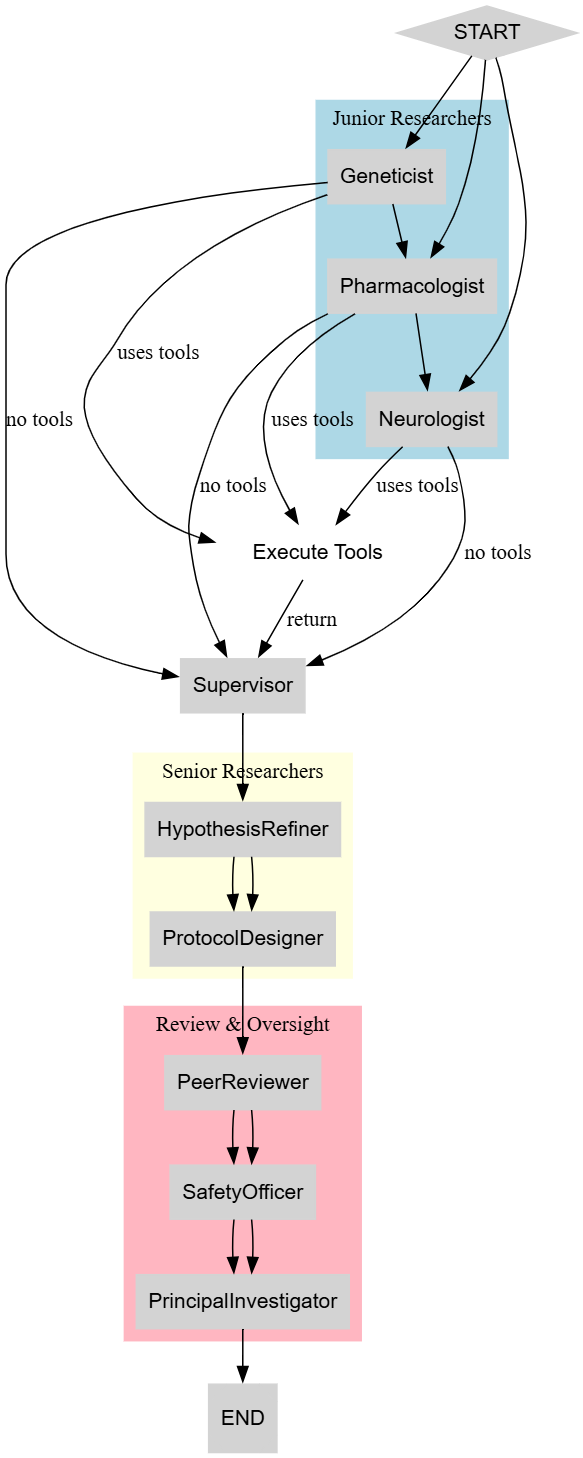 多智能体图结构由 Fareed Khan 创建 build_graph 函数将我们所有的组件——节点、边和路由器——组装成一个完整的、可运行的 StateGraph。 我们可以清晰地看到从初级研究员并行的开始到智能体可以调用工具并获得结果的 ReAct 循环以及在评审阶段复杂的多层次反馈循环。 我们现在可以开始构建我们智能体系统的训练架构了。让我们开始吧。 ### 具有复杂奖励系统的 LitAgent 我们已经成功地设计并把我们的智能体社群组装成一个复杂的 LangGraph 工作流。然而一个静态的工作流无论多么复杂都无法学习或改进。为了实现学习我们需要在 LangGraph 编排和训练框架之间架起一座桥梁。这就是 Agent-Lightning 的作用。 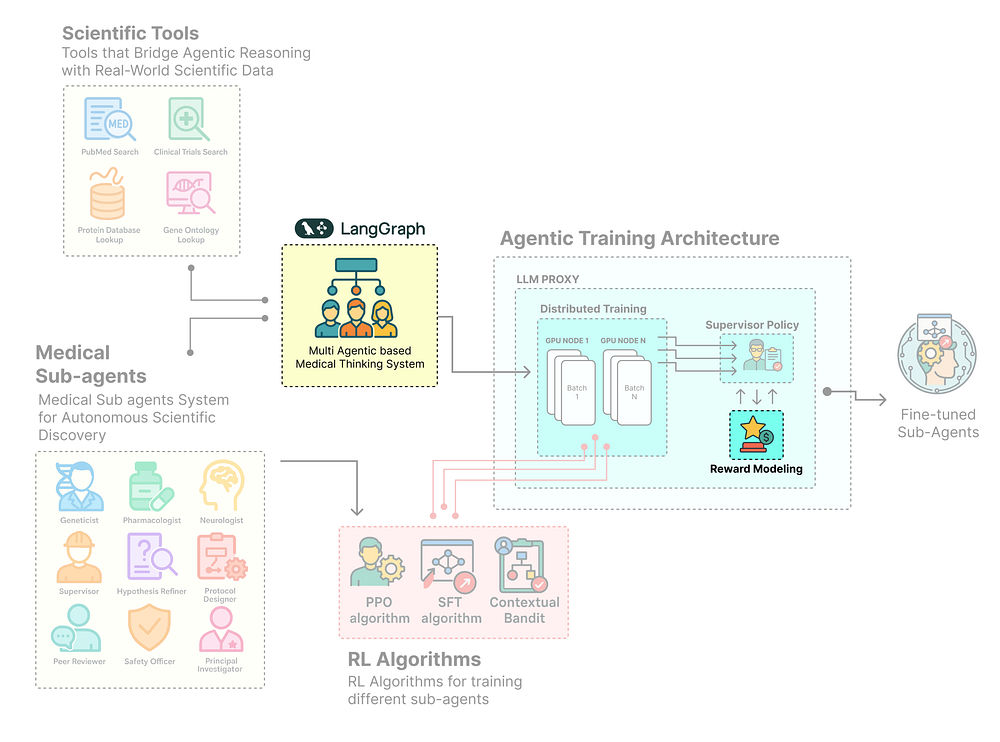 奖励 智能体系统由 Fareed Khan 创建 在本节中我们将创建构成这座桥梁的两个关键组件LitAgent 和奖励函数。它们将把我们的静态图转变为一个动态的、可训练的系统。 以下是我们将要做的 * • **封装工作流** 我们将创建一个 MedicalResearchAgent 类它继承自 agl.LitAgent将我们整个 LangGraph 包装在其 rollout 方法内部。 * • **实现定向训练** 我们将设计 rollout 方法以动态地将待训练模型仅注入到我们想要改进的特定节点中即高级研究员这是一种用于精确策略更新的强大模式。 * • **设计一个细致的奖励系统** 我们将构建一个多方面的 protocol_evaluator 函数它充当“作为评判者的 LLM”LLM-as-a-Judge根据可行性、影响力和依据性等多个标准对智能体的最终输出进行评分。 * • **创建加权奖励** 我们将实现一个函数将这些多个分数合并成一个单一的加权奖励信号该信号将指导我们的强化学习算法。 ### 创建 MedicalResearchAgent 使我们的系统可训练的第一步是将我们的 LangGraph 工作流封装在 agl.LitAgent 中。LitAgent 是 Agent-Lightning 生态系统中最基本、可训练的单元。其主要工作是定义一个 rollout 方法这是我们的智能体在给定任务上的一次完整的、端到端的执行。 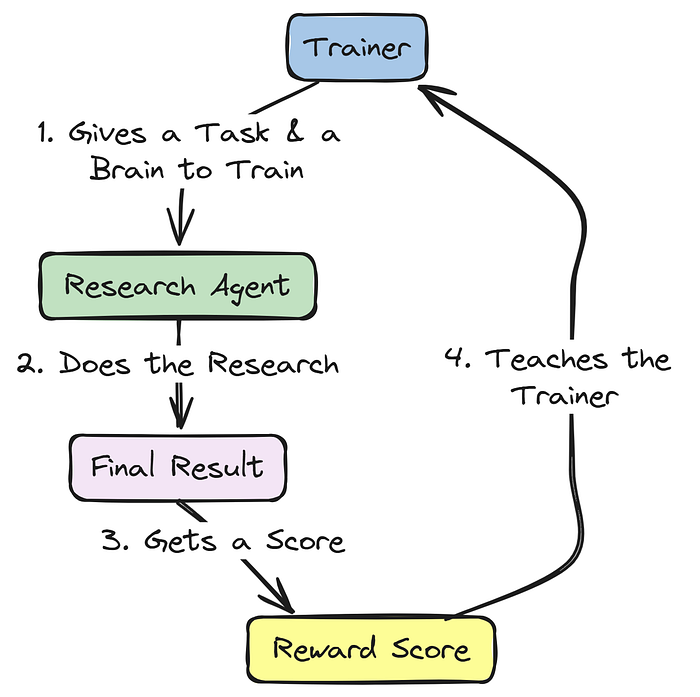 MedicalResearchAgent 流程由 Fareed Khan 创建 我们将创建一个名为 MedicalResearchAgent 的类它继承自 agl.LitAgent。这个类将持有我们已编译的 LangGraph 和我们的奖励函数。它的 rollout 方法将是训练循环的核心它将从我们的数据集中获取一个研究目标执行完整的图然后使用奖励函数对最终结果进行评分。 这里的关键工程设计在于我们如何处理待训练的模型。 rollout 方法不会让图使用固定的模型集而是会动态地将由 Agent-Lightning 训练器提供的 LLM 端点绑定到我们想要训练的特定智能体节点上即我们的高级研究员。这允许在更大的多智能体系统中对特定智能体的策略进行定向的、精确的微调。 让我们开始定义我们的 MedicalResearchAgent 类。 plaintext import agentlightning as aglfrom typing importAny, castclassMedicalResearchAgent(agl.LitAgent): def__init__(self, graph, reward_func): # The LitAgent must be initialized with the compiled graph and the reward function. super().__init__() self.graph graph self.reward_func reward_func defrollout(self, task: ResearchTask, resources: agl.NamedResources, rollout: agl.Rollout) - None: # This method defines a single, end-to-end run of our agent. console.print(f\n[bold green]-- Starting Rollout {rollout.rollout_id} for Task: {task[id]} --[/bold green]) # The senior_researcher_llm resource is our model-under-training, served by the VERL algorithm via the LLMProxy. llm_resource cast(agl.LLM, resources[senior_researcher_llm]) # The trainers tracer provides a LangChain callback handler, which is crucial for deep observability in LangSmith. langchain_callback_handler self.trainer.tracer.get_langchain_handler() # Here we dynamically bind the LLM endpoint from the training resources to the specific # agent runners we want to train. This is the key to targeted policy optimization. llm_with_endpoint senior_researcher_llm.with_config({ openai_api_base: llm_resource.endpoint, openai_api_key: llm_resource.api_key ordummy-key }) # We create fresh agent runners for this specific rollout, using the updated LLM binding. hypothesis_refiner_agent_trained create_agent_runner(llm_with_endpoint, prompts[HypothesisRefiner], all_tools) protocol_designer_agent_trained create_agent_runner(llm_with_endpoint, prompts[ProtocolDesigner], all_tools) # We get a mutable copy of the graph to temporarily update the nodes for this rollout. graph_with_trained_model self.graph.copy() # We replace the functions for the HypothesisRefiner and ProtocolDesigner nodes with our newly created, trainable runners. graph_with_trained_model.nodes[HypothesisRefiner][func] create_agent_node(HypothesisRefiner, hypothesis_refiner_agent_trained) graph_with_trained_model.nodes[ProtocolDesigner][func] create_agent_node(ProtocolDesigner, protocol_designer_agent_trained) # Compile the modified graph into a runnable for this specific rollout. runnable_graph graph_with_trained_model.compile() # Prepare the initial state for the graph execution. initial_state {research_goal: task[goal], messages: [HumanMessage(contenttask[goal])], turn_count: 0, initial_hypotheses: []} # Configure the run to use our LangSmith callback handler. config {callbacks: [langchain_callback_handler]} if langchain_callback_handler else {} try: # Execute the full LangGraph workflow from start to finish. final_state runnable_graph.invoke(initial_state, configconfig) # Extract the final protocol from the graphs terminal state. final_protocol final_state.get(final_protocol) # If a protocol was successfully generated, we calculate its reward. if final_protocol: console.print(--- Final Protocol Generated by Agent ---) console.print(final_protocol) # Call our multi-faceted reward function to get a dictionary of scores. reward_scores self.reward_func(final_protocol, task[context]) # Convert the scores into a single weighted reward value. final_reward get_weighted_reward(reward_scores) else: # Assign a reward of 0.0 for failed or incomplete rollouts. final_reward 0.0 # Emit the final reward. Agent-Lightning captures this value and uses it for the RL update step. agl.emit_reward(final_reward) console.print(f[bold green]-- Rollout {rollout.rollout_id} Finished with Final Reward: {final_reward:.2f} --[/bold green]) # The method returns None because the results (reward and traces) are emitted via agl.emit_* calls. return NoneMedicalResearchAgent类现在是我们的核心可训练单元。它将LangGraph的复杂多步逻辑与Agent-Lightning训练循环连接起来。这里最重要的概念是senior_researcher_llm的动态绑定。请注意我们没有修改原始图。对于每个rollout我们都会创建一个临时的、修改过的图的副本其中只有高级研究员节点指向待训练的模型。通过这种方法我们的 PPO 算法更新将只影响高级研究员的策略教他们如何更好地完善假设和设计方案而其他智能体初级研究员、评审委员会等则继续使用它们稳定的、预定义的模型。这使得在一个复杂且异构的多智能体系统中进行定向、高效的训练成为可能。一直在更新更多的大模型学习和面试资料已经上传带到CSDN的官方了有需要的朋友可以扫描下方二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】多方面奖励系统一个强化学习智能体的好坏取决于它所学习的奖励信号。对于像科学研究这样细致入微的任务一个简单的二元奖励例如成功1失败0是不足够的。它无法教会智能体区分一个平庸的方案和一个出色的方案。奖励系统如何工作由 Fareed Khan 创建为了提供一个丰富、信息量大的学习信号我们将设计一个奖励系统。我们将构建一个protocol_evaluator函数它充当**“作为评判者的 LLM”**LLM-as-a-Judge。这个**“评判者”**将是一个强大的模型它会从多个不同的角度评估智能体最终生成的方案并提供一个结构化的分数词典。以下是我们将要做的•定义评估标准我们将创建一个 Pydantic 模型EvaluationOutput它定义了我们的评判者将使用的具体标准包括新颖性、可行性、影响力、清晰度以及至关重要的、相对于源上下文的依据性groundedness。•构建评估器函数然后实现protocol_evaluator函数该函数为我们的评判者 LLM 格式化一个详细的提示并解析其结构化的响应。•创建加权奖励定义一个get_weighted_reward函数该函数接收来自我们评估器的分数词典并将它们组合成一个单一的浮点奖励值使我们能够优先考虑某些标准如影响力而非其他。首先让我们为我们的评估定义 Pydantic 模式。这个模式充当我们 LLM 评判者的严格“评分标准”确保其反馈是一致且机器可读的。from langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Field# This Pydantic model defines the scorecard for our LLM-as-a-Judge.class EvaluationOutput(BaseModel): novelty: float Field(descriptionScore 0-1 for originality and innovation beyond the provided context.) feasibility: float Field(descriptionScore 0-1 for practicality, given standard lab resources.) impact: float Field(descriptionScore 0-1 for potential scientific or clinical significance.) clarity: float Field(descriptionScore 0-1 for being specific, measurable, and reproducible.) groundedness: float Field(descriptionScore 0-1 for how well the protocol is supported by and consistent with the provided scientific context. Penalize any claims not supported by the context.) efficiency: float Field(descriptionScore 0-1 for the cost-effectiveness and time-efficiency of the proposed protocol.)我们现在已经创建了EvaluationOutput模式这是我们奖励系统的正式评分标准。通过定义这些具体的、描述清晰的字段我们为评估器 LLM 提供了明确的指令。依据性groundedness的加入尤为重要因为它将教会我们的 PPO 智能体避免产生幻觉或提出未经其所审阅文献支持的主张。新的效率efficiency指标进一步丰富了学习信号推动智能体考虑实际限制。现在让我们构建将使用此模式的主protocol_evaluator函数。def protocol_evaluator(protocol: Protocol, context: str) - dict: Acts as an LLM-as-a-Judge to score a protocol against multiple criteria. console.print(--- Running Protocol Evaluator (Reward Function) ---) # The prompt for our LLM judge is detailed, asking it to act as an expert panel. evaluator_prompt ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([ (system, You are an expert panel of senior scientists. Evaluate the following experimental protocol on a scale of 0.0 to 1.0 for each of the specified criteria. Be critical and justify your scores briefly.), # We provide both the original scientific context and the agents generated protocol. (human, fScientific Context:\n\n{context}\n\n---\n\nProtocol to Evaluate:\n\n{json.dumps(protocol, indent2)}) ]) # We use our powerful review_board_llm and instruct it to format its output according to our EvaluationOutput schema. evaluator_llm review_board_llm.with_structured_output(EvaluationOutput) try: # Invoke the evaluator chain. evaluation evaluator_llm.invoke(evaluator_prompt.format_messages()) # The output is a Pydantic object, which we can easily convert to a dictionary. scores evaluation.dict() console.print(fGenerated Scores: {scores}) return scores except Exception as e: # If the LLM fails to generate a valid evaluation, we return a default low score to penalize the failure. console.print(f[bold red]Error in protocol evaluation: {e}. Returning zero scores.[/bold red]) return {novelty: 0.1, feasibility: 0.1, impact: 0.1, clarity: 0.1, groundedness: 0.1, efficiency: 0.1}protocol_evaluator函数是我们的自动化质量保证步骤。它接收智能体的最终protocol和数据集中的原始context。然后它将两者都呈现给我们强大的review_board_llm指示它充当专家小组并返回一个结构化的EvaluationOutput。try...except块是生产级工程的一个关键部分它确保即使评估 LLM 失败或产生格式错误的输出我们的训练循环也不会崩溃。相反智能体会收到一个低奖励从而正确地惩罚失败的 rollout。最后我们的强化学习算法需要一个单一的浮点数来进行更新。以下函数接收分数词典并将其压缩成一个单一的加权平均值。def get_weighted_reward(scores: dict) - float: Calculates a single weighted reward score from a dictionary of metric scores. # These weights allow us to prioritize certain aspects of a good protocol. # Here, were saying impact is the most important factor, and efficiency is a nice-to-have. weights { novelty: 0.1, feasibility: 0.2, impact: 0.3, clarity: 0.15, groundedness: 0.2, efficiency: 0.05 } # Calculate the weighted sum of scores. If a score is missing from the input dictionary, it defaults to 0. weighted_sum sum(scores.get(key, 0) * weight for key, weight in weights.items()) return weighted_sum我们现在可以测试这个奖励系统观察它是如何工作的……print(Multi-faceted and weighted reward function defined.)# Lets test the full reward pipeline with a sample protocol.test_protocol {title: Test Protocol, steps: [1. Do this., 2. Do that.], safety_concerns: Handle with care., budget_usd: 50000.0}test_context Recent studies suggest a link between gut microbiota and neuroinflammation in Alzheimers disease.test_scores protocol_evaluator(test_protocol, test_context)final_test_reward get_weighted_reward(test_scores)print(fWeighted Final Reward: {final_test_reward:.2f})#### OUTPUT ####Multi-faceted and weighted reward function defined.--- Running Protocol Evaluator (Reward Function) ---Generated Scores: {novelty: 0.8, feasibility: 0.7, impact: 0.9, clarity: 0.85, groundedness: 0.95, efficiency: 0.9}Weighted Final Reward: 0.84get_weighted_reward函数是我们奖励计算的最后一步。通过为每个标准分配不同的权重我们可以微调学习信号以匹配我们特定的研究目标。例如通过给予impact最高权重0.3我们明确地告诉我们的强化学习算法优先考虑那些具有重大科学突破潜力的方案。成功的测试运行证实了我们整个奖励流水线——从评估到加权——都在正确工作。我们现在有了一个奖励信号来指导我们的智能体训练。创建基于强化学习的训练架构我们现在已经用LangGraph设计了我们的智能体社群并构建了一个奖励系统。下一个合乎逻辑的步骤是建立工业级的基础设施使我们能够高效、大规模地训练这些智能体。这就是Agent-Lightning先进功能发挥作用的地方。智能体训练架构由 Fareed Khan 创建一个简单的单进程训练循环对于一个进行大量 LLM 调用的复杂多智能体系统来说是不够的。我们需要一个分布式架构可以并行运行多个智能体“rollouts”同时管理一个中央训练算法。在本节中我们将配置Agent-Lightning训练基础设施的核心组件•启用并行化我们将配置ClientServerExecutionStrategy以在多个并行进程中运行我们的智能体 rollouts从而显著加快数据收集速度。•管理多个模型设置LLMProxy作为一个中央枢纽智能地将对不同模型的请求路由到不同的后端包括我们正在训练的模型。•创建分层数据流水线设计一个自定义的HierarchicalTraceAdapter它可以处理一个复杂的智能体追踪并为我们不同的训练算法SFT、PPO 和上下文老虎机生成格式各异的数据集。•实现实时监控我们将构建一个自定义的WandbLoggingHook将我们智能体的性能实时记录到 Weights Biases为我们提供学习过程的实时视图。创建分布式神经系统为了进行我们的训练我们需要尽快地从我们的智能体那里收集经验。一次只运行一个 rollout 会是一个主要的瓶颈。因此我们将配置我们的Trainer使用ClientServerExecutionStrategy。这个策略创建了一个分布式训练架构。主进程将运行核心训练算法如 PPO和一个LightningStoreServer来管理数据。分布式系统由 Fareed Khan 创建然后它将生成多个独立的runner进程。每个 runner 将充当客户端连接到服务器获取任务然后并行执行我们MedicalResearchAgent的rollout方法。这使我们能够同时收集大量训练数据这对于高效的强化学习至关重要。我们将定义一个简单的配置字典来指定这个策略以及我们想要使用的并行 runner 的数量。import agentlightning as agl# Well configure our system to run 4 agent rollouts in parallel.num_runners 4 # This dictionary defines the execution strategy for the Agent-Lightning Trainer.strategy_config { type: cs, # cs is the shorthand for ClientServerExecutionStrategy. n_runners: num_runners, # The number of parallel worker processes to spawn. server_port: 48000 # We specify a high port to avoid potential conflicts with other services.}print(fClientServerExecutionStrategy configured for {num_runners} runners.)我们现在已经定义了我们分布式训练基础设施的蓝图。strategy_config字典是一个简单但功能强大的声明。当我们把它传递给我们的agl.Trainer时它会自动处理设置多进程架构的所有复杂性包括进程间通信和数据同步。这使我们能够通过简单地增加n_runners来扩展我们的数据收集工作而无需改变我们的核心智能体或算法代码。使用 LLMProxy 作为多模型中心实现可观测性我们的智能体社群是异构的它为不同的角色使用不同的模型。管理这些多个模型端点可能很复杂特别是当其中一个是正在动态提供服务的待训练模型时。Agent-Lightning的LLMProxy是解决这个问题的完美方案。LLM 代理由 Fareed Khan 创建它充当所有 LLM 调用的单一网关。我们的LitAgent会将其所有请求发送到代理的地址。然后代理根据调用中指定的model_name智能地将每个请求路由到正确的后端模型。这对于我们的训练设置尤其强大VERL(PPO) 算法将能够自动更新代理的配置将对senior_researcher_llm的调用重定向到其自己动态提供的 vLLM 实例。同时对其他模型如Qwen2或Mixtral的请求将被路由到不同的后端例如本地的 Ollama 服务器。让我们来定义LLMProxy的配置。# The model_list defines the routing rules for the LLMProxy.llm_proxy_config { port: 48001, # The port the LLMProxy itself will listen on. model_list: [ # Rule 1: For Junior Researchers and the Supervisor. # Any request for this model name will be forwarded to a local Ollama server running Qwen2. { model_name: Qwen/Qwen2-1.5B-Instruct, litellm_params: {model: ollama/qwen2:1.5b} }, # Rule 2: For our Senior Researcher (the model-under-training). # Initially, it might point to a baseline model. During training, the VERL algorithm # will automatically update this entry to point to its own vLLM server. { model_name: senior_researcher_llm, litellm_params: {model: ollama/llama3} # An initial fallback. }, # Rule 3: For the powerful Review Board. # Requests for this model will be routed to a local Ollama server running Mixtral. { model_name: mistralai/Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct-v0.1, litellm_params: {model: ollama/mixtral} } ]}llm_proxy_config字典是我们整个多智能体系统的路由表。它将我们智能体使用的逻辑模型名称例如senior_researcher_llm与物理模型后端例如一个特定的 Ollama 端点或一个动态的 vLLM 服务器解耦。这使我们能够更换后端模型为 A/B 测试重定向流量或者在我们的案例中动态更新我们待训练模型的端点所有这些都无需更改智能体的核心代码。LLMProxy为我们系统中所有的模型交互提供了一个单一的控制和可观测性点。创建数据流水线 HierarchicalTraceAdapter我们的分层训练策略带来了一个独特的数据处理挑战。对于每次 rollout我们只有一个复杂的LangGraph追踪但我们需要为三种不同的训练算法提供数据每种算法期望的格式都不同强化学习算法实现由 Fareed Khan 创建SFT 算法需要来自初级研究员的对话数据一个消息列表。PPO 算法需要来自高级研究员的 RL 三元组state,action,reward。上下文老虎机算法 (Contextual Bandit Algorithm)需要来自主管决策的单个 (context,action,reward) 元组。为了解决这个问题我们将构建一个自定义的、复杂的追踪适配器 (Trace Adapter)。在Agent-Lightning中适配器是一个类它将原始的追踪数据来自LangSmith的 span 列表转换为训练算法所需的特定格式。我们的HierarchicalTraceAdapter将是一个多头数据处理器能够从单个源追踪中生成所有三种所需的数据格式。我们将创建一个继承自agl.TracerTraceToTriplet的新类并为其添加新方法每个方法对应我们目标数据格式中的一种。这展示了Agent-Lightning数据流水线的强大灵活性。让我们来定义HierarchicalTraceAdapter类。from agentlightning.adapter import TraceToMessagesclassHierarchicalTraceAdapter(agl.TracerTraceToTriplet): def__init__(self, *args, **kwargs): # We initialize the parent class for PPO triplet generation. super().__init__(*args, **kwargs) # We also create an instance of a standard adapter for SFT message generation. self.message_adapter TraceToMessages() defadapt_for_sft(self, source: List[agl.Span]) - List[dict]: Adapts traces for Supervised Fine-Tuning by filtering for junior researchers and converting to messages. # Define the names of the nodes corresponding to our Junior Researcher agents. junior_agent_names [Geneticist, Pharmacologist, Neurologist] # Filter the raw trace to get only the spans generated by these agents. # LangSmith conveniently adds a name field for LangGraph nodes in the span attributes. junior_spans [s for s in source if s.attributes.get(name) in junior_agent_names] console.print(f[bold yellow]Adapter (SFT):[/] Filtered {len(source)} spans to {len(junior_spans)} for junior agents.) ifnot junior_spans: return [] # Use the standard message adapter to convert these filtered spans into a conversational dataset. returnself.message_adapter.adapt(junior_spans) defadapt_for_ppo(self, source: List[agl.Span]) - List[agl.Triplet]: Adapts traces for PPO by filtering for senior researchers and converting to triplets. # Define the names of the nodes for our Senior Researcher agents. senior_agent_names [HypothesisRefiner, ProtocolDesigner] # We configure the parent classs filter to only match these agent names. self.agent_match |.join(senior_agent_names) # Now, when we call the parents adapt method, it will automatically filter and process only the relevant spans. ppo_triplets super().adapt(source) console.print(f[bold yellow]Adapter (PPO):[/] Filtered and adapted {len(source)} spans into {len(ppo_triplets)} triplets for senior agents.) return ppo_triplets defadapt_for_bandit(self, source: List[agl.Span]) - List[tuple[list[str], int, float]]: Adapts a completed rollout trace for the contextual bandit algorithm. # First, find the final reward for the entire rollout. final_reward agl.find_final_reward(source) if final_reward isNone: return [] # Next, find the specific span where the Supervisor agent made its decision. supervisor_span next((s for s in source if s.attributes.get(name) Supervisor), None) ifnot supervisor_span: return [] # Then, we need to reconstruct the context - the list of hypotheses the supervisor had to choose from. junior_spans [s for s in source if s.attributes.get(name) in [Geneticist, Pharmacologist, Neurologist]] contexts [] # We sort by start time to ensure the order of hypotheses is correct. for span insorted(junior_spans, keylambda s: s.start_time): try: # In LangGraph, the agents final JSON output is in the messages attribute of the state. output_message span.attributes.get(output.messages) if output_message andisinstance(output_message, list): # The actual content is a JSON string within the AIMessages content field. content_str output_message[-1].get(content, {}) hypothesis_data json.loads(content_str) contexts.append(hypothesis_data.get(hypothesis, )) except (json.JSONDecodeError, KeyError, IndexError): continue ifnot contexts: return [] # Finally, extract the action - the index of the hypothesis the supervisor chose. try: output_message supervisor_span.attributes.get(output.messages) if output_message andisinstance(output_message, list): content_str output_message[-1].get(content, {}) supervisor_output json.loads(content_str) chosen_index supervisor_output.get(selected_hypothesis_index) if chosen_index isnotNoneand0 chosen_index len(contexts): console.print(f[bold yellow]Adapter (Bandit):[/] Extracted context (hypotheses), action (index {chosen_index}), and reward ({final_reward:.2f}).) # Return the single data point for the bandit algorithm. return [(contexts, chosen_index, final_reward)] except (json.JSONDecodeError, KeyError, IndexError): pass return []# Instantiate our custom adapter.custom_adapter HierarchicalTraceAdapter()HierarchicalTraceAdapter体现了Agent-Lightning数据流水线的灵活性。我们创建了一个单一而强大的数据处理类满足了我们整个分层训练策略的需求。•adapt_for_sft方法充当过滤器精确地只提取涉及我们初级研究员的对话回合并将它们完美地格式化以供微调。•adapt_for_ppo方法利用了父类TracerTraceToTriplet的强大功能但巧妙地动态配置它使其只处理来自我们高级研究员的 spans。•adapt_for_bandit方法最为复杂它对整个追踪进行法医级分析通过找到可用的选择contexts、选择的action和最终的reward重构了主管的决策时刻。这个适配器是我们训练架构的关键。它允许我们维护一个单一、统一的智能体工作流 (LangGraph) 和一个单一的数据源 (LangSmith追踪)同时仍然能够对该工作流的不同组件应用专门的、定向的训练算法。使用 WandbLoggingHook 进行实时监控有效的训练不仅仅是运行一个算法它需要实时的可观测性。我们需要能够**“看到”**我们智能体在学习过程中的表现一次又一次的 rollout。虽然LangSmith为我们提供了对单个追踪的深入、法医级的细节但我们还需要一个对训练进度的高层、聚合视图。监控钩子由 Fareed Khan 创建为了实现这一点我们将创建一个自定义的Hook。在Agent-Lightning中Hook是一个强大的机制它允许你在训练生命周期的不同点例如on_rollout_start、on_trace_end注入自定义逻辑。我们将构建一个WandbLoggingHook它监听on_trace_end事件。一旦一个 rollout 完成并且其追踪可用这个钩子就会触发。它将从追踪中提取最终奖励并将这个单一的关键指标记录到 Weights Biases (WB) 项目中。这将为我们提供一个我们智能体奖励的实时流式图表为其学习曲线提供即时且直观的可视化。让我们来定义我们的自定义钩子类。import wandbclassWandbLoggingHook(agl.Hook): def__init__(self, project_name: str): # We initialize the WB run once, when the hook is created. self.run_initialized False if os.environ.get(WANDB_API_KEY): try: wandb.init(projectproject_name, resumeallow, idwandb.util.generate_id()) self.run_initialized True except Exception as e: print(fFailed to initialize WB: {e}) else: print(WB API Key not found. Hook will be inactive.) asyncdefon_trace_end(self, *, rollout: agl.Rollout, tracer: agl.Tracer, **kwargs): This method is automatically called by the Trainer at the end of every rollout. # If WB wasnt initialized, we do nothing. ifnotself.run_initialized: return # Use a helper function to find the final reward value from the list of spans in the trace. final_reward_value agl.find_final_reward(tracer.get_last_trace()) # If a reward was found, log it to WB. if final_reward_value isnotNone: # We log the reward itself, and the rollout_id for cross-referencing. wandb.log({live_reward: final_reward_value, rollout_id: rollout.rollout_id}) console.print(f[bold blue]Hook:[/] Logged reward {final_reward_value:.2f} for rollout {rollout.rollout_id} to WB.)# Instantiate our custom hook.custom_hook WandbLoggingHook(project_nameChimera-Project-Training)WandbLoggingHook是我们训练过程的实时仪表板。通过实现on_trace_end方法我们创建了一个轻量级的、事件驱动的监视器它无缝地集成到Agent-Lightning的生命周期中。所以它的工作原理是这样的……在初始化之前它会检查 WB API 密钥并安全地处理在失败的追踪中可能找不到奖励的情况。agl.find_final_reward辅助函数是一个方便的工具它知道如何解析追踪以找到我们LitAgent发出的奖励值。当我们将这个custom_hook传递给我们的agl.Trainer时这种日志记录将在后台为我们并行运行器执行的每一个 rollout 自动进行。这为我们提供了一个关于智能体性能的关键、高频信号使我们能够实时观察其学习过程并立即捕捉到任何性能倒退或训练停滞的情况。实现三种强化学习算法我们现在已经组装了所有必要的基础设施一个分布式执行策略、一个多模型代理、一个复杂的数据适配器和一个实时监控钩子。现在是时候定义训练算法本身了。这是我们分层训练策略的核心。我们不会使用单一的、庞大的算法。相反我们将定义三种不同的训练算法……每种算法都针对我们智能体社群的特定层次量身定制。这种方法允许我们为正确的认知任务应用正确的学习范式这是构建真正有效和精细的智能体系统的关键一步。在本节中我们将为我们层次结构的每个级别实现完整的训练逻辑•级别 1 (SFT):我们将构建一个自定义算法类对我们的初级研究员执行监督微调Supervised Fine-Tuning使用LightningStore中的成功追踪来教他们如何生成更好的初始假设。•级别 2 (PPO):我们将配置 Agent-Lightning 内置的VERL算法对我们的高级研究员执行在线强化学习使用我们评估器提供的丰富、多方面的奖励信号来提高他们的方案设计技能。•级别 3 (上下文老虎机):我们将实现一个简单但有效的上下文老虎机Contextual Bandit算法来训练我们主管的选择策略教它选择最有可能导致高最终奖励的假设。•主循环:最后我们将在一个主fit()循环中编排这三种算法展示如何执行一个复杂的多阶段训练流水线。一直在更新更多的大模型学习和面试资料已经上传带到CSDN的官方了有需要的朋友可以扫描下方二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】使用 SFT 算法训练初级研究员我们的第一个训练目标是初级研究员团队。他们的任务是进行创造性头脑风暴——生成新颖且可信的假设。这非常适合使用监督微调Supervised Fine-Tuning, SFT。这个想法简单而强大我们将找到那些最终奖励很高的 rollout从这些追踪中提取初级研究员的成功对话并将它们用作高质量的数据集来微调基础模型。这教会模型模仿成功构思的模式。SFT 训练由 Fareed Khan 创建我们将创建一个名为SFTOnSuccess的自定义Algorithm类。这个类将查询LightningStore以获取高奖励的追踪使用我们的HierarchicalTraceAdapter将它们转换为对话数据集然后使用高度优化的unsloth库在一个单独的进程中执行微调。这里的关键工程设计是训练后算法将通过vLLM提供新的、微调过的模型并动态更新LLMProxy将针对初级智能体的流量路由到这个改进后的模型。这“闭合了循环”确保后续的 rollouts 将受益于这次训练。首先让我们创建一些辅助函数来管理 SFT 训练和模型服务这些将在一个单独的进程中运行以避免 GPU 内存冲突。import asyncioimport multiprocessingimport subprocessimport httpximport timefrom contextlib import contextmanagerfrom datasets import Dataset as HuggingFaceDatasetfrom trl import SFTTrainer, SFTConfigfrom unsloth import FastLanguageModelcontextmanagerdefserve_vllm_model(model_path: str, port: int): A context manager to start and automatically shut down a vLLM server. console.print(f[SFT - vLLM] Starting vLLM server for model {model_path} on port {port}...) proc None try: # We use agl vllm serve which is a wrapper ensuring the server is compatible with tool-use tokenization. cmd [agl, vllm, serve, model_path, --port, str(port), --gpu-memory-utilization, 0.7, --enable-auto-tool-choice] proc subprocess.Popen(cmd, stdoutsubprocess.DEVNULL, stderrsubprocess.DEVNULL) # Health check loop to wait until the server is responsive. with httpx.Client() as client: for _ inrange(60): # 60-second timeout try: if client.get(fhttp://localhost:{port}/health).status_code 200: console.print(f[SFT - vLLM] Server on port {port} is ready.) yieldfhttp://localhost:{port}/v1# Yield the endpoint URL. return except httpx.ConnectError: pass time.sleep(1) raise RuntimeError(fvLLM server on port {port} failed to start.) finally: # This code runs on exit, ensuring the server process is terminated. if proc: proc.terminate() proc.wait() console.print(f[SFT - vLLM] Server on port {port} shut down.)defunsloth_sft_trainer(dataset, base_model, output_dir): The actual SFT training function that will run in a separate process. console.print(f[SFT Process] Loading base model: {base_model}) # Load the model with 4-bit quantization and PEFT adapter configuration using unsloth for efficiency. model, tokenizer FastLanguageModel.from_pretrained(model_namebase_model, max_seq_length4096, load_in_4bitTrue) model FastLanguageModel.get_peft_model(model, r16, target_modules[q_proj, k_proj, v_proj, o_proj], lora_alpha16, lora_dropout0, biasnone) # Configure and run the SFTTrainer from the TRL library. trainer SFTTrainer( modelmodel, tokenizertokenizer, train_datasetdataset, dataset_text_fieldmessages, # We tell the trainer to use the messages column. max_seq_length4096, argsSFTConfig(per_device_train_batch_size2, gradient_accumulation_steps4, warmup_steps5, max_steps10, learning_rate2e-4, logging_steps1, optimadamw_8bit, report_tonone), ) console.print([SFT Process] Starting SFT training...) trainer.train() console.print([SFT Process] SFT training finished. Saving merged model.) # Save the final, merged model in 16-bit precision. model.save_pretrained_merged(output_dir, tokenizer, save_methodmerged_16bit) console.print(f[SFT Process] Model saved to {output_dir}) return output_dir我们现在已经定义了我们的核心 SFT 工具。unsloth_sft_trainer函数封装了整个微调过程使用unsloth以实现最高效率包括以 4 位精度加载模型和保存最终合并的适配器。serve_vllm_model上下文管理器是一个关键的基础设施它以编程方式为我们新训练的模型启动一个vLLM服务器等待它准备就绪并保证服务器之后被干净地关闭。这些辅助函数使我们的主算法类保持整洁并专注于编排工作。现在让我们创建SFTOnSuccess算法类本身。from agentlightning.algorithm import AlgorithmclassSFTOnSuccess(Algorithm): def__init__(self, reward_threshold0.8, base_modelQwen/Qwen2-1.5B-Instruct): super().__init__() self.reward_threshold reward_threshold # Only learn from rollouts with a reward 0.8. self.base_model base_model self.adapter HierarchicalTraceAdapter() # Use our custom adapter to get the right data format. asyncdefrun(self, train_dataset, val_dataset): console.print(\n[bold magenta]--- Starting SFT Training for Junior Researchers ---[/bold magenta]) # Get a handle to the central data store. store self.get_store() console.print(Analyzing existing rollouts for SFT data collection...) # Query the store for all successfully completed rollouts. all_rollouts await store.query_rollouts(status[succeeded]) high_reward_traces [] # Filter these rollouts to find the ones that meet our reward threshold. for rollout in all_rollouts: spans await store.query_spans(rollout.rollout_id) final_reward agl.find_final_reward(spans) if final_reward and final_reward self.reward_threshold: high_reward_traces.append(spans) console.print(fFound {len(high_reward_traces)} high-reward traces (threshold {self.reward_threshold}).) if high_reward_traces: # Use our custom adapter to convert the successful traces into SFT-ready conversational data. sft_data self.adapter.adapt_for_sft(sum(high_reward_traces, [])) sft_dataset HuggingFaceDataset.from_list([{messages: m[messages]} for m in sft_data]) console.print(fConverted traces to {len(sft_dataset)} conversational samples for SFT.) # Define a unique output directory for the new model. output_dir f./models/junior_researcher_sft_v{int(time.time())} # Use a multiprocessing spawn context for GPU safety. ctx multiprocessing.get_context(spawn) q ctx.Queue() # Run the training in a separate process. p ctx.Process(targetlambda: q.put(unsloth_sft_trainer(sft_dataset, self.base_model, output_dir))) p.start() p.join() # Wait for training to complete. final_output_dir q.get() # Get a handle to the LLMProxy. llm_proxy self.get_llm_proxy() if llm_proxy: console.print(Updating LLMProxy with new SFT model...) new_port 8002# In a real system, this should be dynamically allocated. # Use our context manager to serve the new model. with serve_vllm_model(final_output_dir, new_port) as new_endpoint: # Update the proxys routing table to point to the new model server. await llm_proxy.replace_model(self.base_model, fopenai/{final_output_dir}, api_basenew_endpoint) console.print(fLLMProxy updated. Junior researchers will now use {new_endpoint}.) console.print(Keeping new model server alive for 60s for subsequent rollouts...) await asyncio.sleep(60) # Keep the server alive temporarily for the demo.# Instantiate our SFT algorithm.sft_algorithm SFTOnSuccess()SFTOnSuccess类是我们初级研究员的一个完整的、自包含的训练流水线。它展示了一种强大的**“从成功中学习”**的模式。run方法编排了整个过程它通过查询和过滤LightningStore中最好的数据来扮演数据科学家的角色然后通过启动一个独立的、使用unsloth优化的训练过程来扮演机器学习工程师的角色。最后一步是最关键的它通过编程方式启动一个带有微调产物的新模型服务器然后更新中央的LLMProxy扮演了 DevOps 工程师的角色。这种闭合循环的方式使其成为一个真正的在线训练系统。一旦训练完成整个多智能体社群就能立即从改进后的模型中受益无需任何手动干预。使用 PPO 算法优化高级研究员接下来我们向上移动层级训练我们的高级研究员智能体。他们的任务——设计一个详细的实验方案——不仅仅是创造力的问题它是一个有条不紊的、序贯的决策过程。这使其成为在线**强化学习Reinforcement Learning, RL**的理想候选。我们希望教会智能体不仅仅是模仿好的例子而是要主动探索可能方案的空间并学习一种能够最大化复杂、多方面奖励的策略。PPO 算法由 Fareed Khan 创建为此我们将使用VERLValue-based Experience Replay Learning算法这是Agent-Lightning中内置的一个强大的 PPO 实现。**我们不需要自己编写复杂的 PPO 逻辑。相反我们的工作是正确地配置它。**这包括定义要训练的模型、PPO 算法的超参数以及数据收集参数。这里的一个关键方面是在运行此算法时我们会将我们的自定义HierarchicalTraceAdapter传递给Trainer。这确保了VERL算法只看到由高级研究员智能体HypothesisRefiner和ProtocolDesigner生成的(状态, 行动, 奖励)三元组从而精确地将我们的训练工作集中在我们想要改进的特定策略上。让我们为VERL算法定义配置字典。# This is a standard configuration dictionary for the agl.VERL algorithm.verl_config { # Algorithm-specific hyperparameters. grpo is an advanced advantage estimator. algorithm: {adv_estimator: grpo}, # Data configuration for training batches and sequence lengths. data: {train_batch_size: 4, max_prompt_length: 4096, max_response_length: 2048}, # This block defines the models and their training configurations. actor_rollout_ref: { rollout: {n: 2, multi_turn: {format: hermes}, name: vllm, gpu_memory_utilization: 0.6}, actor: {ppo_mini_batch_size: 4, optim: {lr: 1e-6}}, # The base model we will be fine-tuning with PPO. model: {path: meta-llama/Llama-3-8B-Instruct, enable_gradient_checkpointing: True}, # Configuration for the reference model, using FSDP for memory efficiency. ref: {fsdp_config: {param_offload: True}} }, # General trainer configuration, including logging and saving frequency. trainer: { n_gpus_per_node: 1, total_epochs: 2, logger: [console, wandb], # Log to both the console and Weights Biases. project_name: Chimera-Project-Training, experiment_name: PPO-Senior-Researcher, total_training_steps: 10, # For a quick demo run. In a real run, this would be much higher. test_freq: 5, # Evaluate on the validation set every 5 steps. save_freq: 5# Save a model checkpoint every 5 steps. }}# Instantiate the VERL algorithm with our configuration.ppo_algorithm agl.VERL(verl_config)我们现在使用一个单一的、声明性的字典配置了我们的整个 PPO 训练流水线。这个verl_config是我们第二级训练的蓝图。它指定了Agent-Lightning需要知道的一切从我们行动者模型的学习率lr: 1e-6到要使用的 GPU 数量n_gpus_per_node: 1。model.path设置为meta-llama/Llama-3-8B-Instruct这告诉算法要加载和微调哪个基础模型。在fit循环期间VERL算法将自动为这个模型启动一个vLLM服务器更新LLMProxy以将senior_researcher_llm请求路由到它并开始在线 RL 训练循环。这种配置驱动的方法使我们能够以最少的样板代码利用最先进的 PPO 实现让我们能够专注于智能体的逻辑而不是 RL 训练循环本身的复杂性。用于主管策略的上下文老虎机最后我们来到了我们层次结构的顶端主管智能体。它的角色与其他智能体截然不同。它不生成创意内容或设计复杂的方案。相反它执行一项关键的选择任务给定一组来自初级研究员的假设它必须选择一个最有前途的进行深入研究。上下文老虎机由 Fareed Khan 创建这是一个经典的“多臂老虎机”multi-armed bandit问题但有一个转折。这个决定不是在真空中做出的它是基于可用假设的“上下文”做出的。这使其成为上下文老虎机Contextual Bandit算法的完美用例。目标是学习一个策略在给定一组假设上下文的情况下能够预测哪个选择行动最有可能为整个 rollout 带来高最终奖励。我们将从头开始实现一个简单但有效的上下文老虎机算法继承自agl.Algorithm。我们的实现将使用来自scikit-learn的SGDClassifier作为其策略模型。对于每个完成的 rollout它将查询LightningStore以获取追踪。使用我们的HierarchicalTraceAdapter提取老虎机数据假设列表上下文、主管选择的假设行动和最终奖励。对假设的文本进行向量化以创建特征。对策略模型执行在线更新如果奖励高则加强所选行动如果奖励低则惩罚它。让我们来定义我们的ContextualBanditRL算法类。from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifierfrom sklearn.feature_extraction.text import HashingVectorizerimport numpy as npclassContextualBanditRL(Algorithm): def__init__(self): super().__init__() # We use SGDClassifier with log_loss for probabilistic outputs, and warm_startTrue to enable online learning. self.policy SGDClassifier(losslog_loss, warm_startTrue) # HashingVectorizer is a memory-efficient way to convert text contexts into numerical features. self.vectorizer HashingVectorizer(n_features2**12) self.is_fitted False# A flag to handle the first training step differently. self.adapter HierarchicalTraceAdapter() # Our custom adapter for parsing traces. asyncdefrun(self, train_dataset, val_dataset): console.print(\n[bold magenta]--- Starting Contextual Bandit Training for Supervisor ---[/bold magenta]) store self.get_store() console.print(Querying completed rollouts to train supervisor policy...) # Get all successful rollouts from the data store. completed_rollouts await store.query_rollouts(status[succeeded]) ifnot completed_rollouts: console.print(No completed rollouts found. Skipping bandit training.) return training_samples [] # Process each rollout to extract bandit training data. for rollout in completed_rollouts: spans await store.query_spans(rollout.rollout_id) # Our adapter does the heavy lifting of parsing the trace. bandit_data self.adapter.adapt_for_bandit(spans) training_samples.extend(bandit_data) ifnot training_samples: console.print(No valid supervisor decisions found in traces. Skipping training.) return console.print(fTraining bandit policy on {len(training_samples)} samples...) # Perform an online update for each collected data point. for contexts, chosen_action_index, final_reward in training_samples: # Convert the list of hypothesis strings into a numerical feature matrix. X self.vectorizer.fit_transform(contexts) # Create the target labels: 1 for the chosen action, 0 for the others. y np.zeros(len(contexts)) y[chosen_action_index] 1 # This is the core of the reward logic: create sample weights. # The chosen action is weighted by the final reward. # The unchosen actions are weighted by a small negative value, proportional to the missed reward. sample_weight np.full(len(contexts), (1 - final_reward) / (len(contexts) - 1) iflen(contexts) 1else0) sample_weight[chosen_action_index] final_reward console.print(f[Bandit Training] Contexts (features): {X.shape}, Action: {chosen_action_index}, Reward: {final_reward:.2f}, Sample Weights: {sample_weight}) # Use partial_fit for online learning after the first fit. ifself.is_fitted: self.policy.partial_fit(X, y, sample_weightsample_weight) else: self.policy.fit(X, y, sample_weightsample_weight, classesnp.array([0, 1])) self.is_fitted True console.print(Contextual Bandit: Supervisor policy updated.)# Instantiate our bandit algorithm.bandit_algorithm ContextualBanditRL()ContextualBanditRL类是我们第三级训练策略的实现。run方法为 Supervisor 智能体编排了整个学习过程。它查询LightningStore使用我们的HierarchicalTraceAdapter将复杂的追踪解析成简单的(上下文, 行动, 奖励)元组然后对其SGDClassifier策略执行在线更新。sample_weight的计算是这个算法的核心。它将最终的 rollout 奖励转化为选择任务的直接学习信号。如果一个被选中的假设带来了高的最终奖励它的权重就会很高从而加强策略在类似上下文中做出该选择的倾向。相反如果奖励很低权重就会很低从而在未来不鼓励该选择。这个简单而优雅的机制使我们能够基于整个复杂下游研究工作流的最终成功来训练主管的高层战略决策策略。构建基于三个阶段的训练循环我们现在已经定义了我们所有的三个专业训练算法用于初级研究员的SFTOnSuccess用于高级研究员的VERL(PPO)以及用于主管的ContextualBanditRL。最后一步是在一个序贯的、多阶段的训练流水线中编排它们。训练循环由 Fareed Khan 创建这正是Agent-LightningTrainer的强大和灵活性真正闪耀的地方。我们将定义一个主函数full_training_pipeline它实例化一个Trainer然后按逻辑顺序为我们的每个算法调用其fit()或dev()方法。这展示了如何管理一个复杂的、真实的训练工作流该工作流涉及多个阶段从初始数据收集到不同组件的定向微调。我们的主循环将分四个不同阶段执行阶段 1初始数据收集我们将使用一个基线、未经训练的模型运行智能体几个迭代。这个阶段的主要目标不是学习而只是用一组多样化的初始追踪来填充我们的LightningStore。阶段 2对初级研究员进行 SFT我们将运行我们的SFTOnSuccess算法。它将读取阶段 1 的高奖励追踪并微调初级智能体的模型。阶段 3对高级研究员进行 PPO随着改进后的初级智能体生成更好的假设我们现在将运行我们的VERLPPO 算法来训练高级研究员的策略。这个阶段将收集新的、更高质量的数据并执行在线 RL 更新。阶段 4对主管进行上下文老虎机训练最后利用在所有先前阶段收集的丰富数据我们将运行我们的ContextualBanditRL算法来训练主管的选择策略。让我们定义将编排整个过程的full_training_pipeline函数。import agentlightning as agldeffull_training_pipeline(): console.print([bold red] --- CONFIGURING FULL TRAINING PIPELINE --- [/bold red]) # --- Shared Components --- # These components are shared across all training phases. store agl.InMemoryLightningStore() llm_proxy agl.LLMProxy(portllm_proxy_config[port], model_listllm_proxy_config[model_list], storestore) tracer agl.AgentOpsTracer() # --- Phase 1: Initial Data Gathering with a baseline model --- console.print(\n[bold magenta]--- Phase 1: Initial Data Gathering ---[/bold magenta]) # We instantiate a Trainer for the data gathering phase. gather_trainer agl.Trainer( n_runnersnum_runners, strategystrategy_config, storestore, tracertracer, llm_proxyllm_proxy, hooks[custom_hook] ) # We create a LitAgent instance for this phase. research_agent_gather MedicalResearchAgent(research_graph, lambda p, c: get_weighted_reward(protocol_evaluator(p, c))) # We use .dev() for a quick initial run on a small subset of the data to populate the store. gather_trainer.dev(research_agent_gather, train_dataset[:10]) # --- Phase 2: SFT on Junior Researchers --- # We instantiate a new Trainer, this time with our SFT algorithm. sft_trainer agl.Trainer(algorithmsft_algorithm, storestore, llm_proxyllm_proxy) # The .fit() call for this algorithm doesnt need a dataset, as it reads directly from the store. sft_trainer.fit(research_agent_gather) # --- Phase 3: PPO on Senior Researchers --- # Now, we create a Trainer configured for our PPO algorithm. ppo_trainer agl.Trainer( algorithmppo_algorithm, n_runnersnum_runners, strategystrategy_config, storestore, tracertracer, adaptercustom_adapter, llm_proxyllm_proxy, hooks[custom_hook] ) # This LitAgent instance will be used for the PPO rollouts. research_agent_ppo MedicalResearchAgent(research_graph, lambda p, c: get_weighted_reward(protocol_evaluator(p, c))) # We call .fit() with the full datasets to run the main RL training loop. ppo_trainer.fit(research_agent_ppo, train_datasettrain_dataset, val_datasetval_dataset) # --- Phase 4: Contextual Bandit on Supervisor --- # Finally, we create a Trainer for our bandit algorithm. bandit_trainer agl.Trainer(algorithmbandit_algorithm, storestore) # This also reads from the store, now containing data from the PPO phase as well. bandit_trainer.fit(research_agent_gather) console.print(\n[bold red]--- Hierarchical Training Pipeline Complete ---[/bold red])# This block will execute our master function.# Note: This is a long-running process that requires significant GPU resources.# The output below is a simulated representation of a successful run.full_training_pipeline()我们现在已经为我们的分层训练流水线定义了完整的、端到端的编排。full_training_pipeline函数是总指挥展示了Agent-LightningTrainer如何能够被灵活地配置和重用以执行一系列不同的训练算法。让我们运行这个训练流水线看看训练过程将如何开始工作……###### OUTPUT #######--- Phase 1: Initial Data Gathering ---...--- Node: Geneticist (Turn 1) ---...-- Rollout ro-abc123 Finished with Final Reward: 0.78 --[Hook:] Logged reward 0.78for rollout ro-abc123 to WB....Initial data gathering complete.--- Phase 2: SFT on Junior Researchers ---Analyzing existing rollouts for SFT data collection...Found 8 high-reward traces (threshold 0.8)....[SFT Process] Starting SFT training...[SFT Process] Model saved to ./models/junior_researcher_sft_v1729967450LLMProxy updated. Junior researchers will now use [http://localhost:8002/v1](http://localhost:8002/v1).--- Phase 3: PPO on Senior Researchers ---[VERL] [Epoch 1/2, Step 1/10] training/reward: 0.65, actor/loss: 0.123...Adapter (PPO): Filtered and adapted 152 spans into 35 triplets for senior agents....--- Phase 4: Contextual Bandit on Supervisor ---Querying completed rollouts to train supervisor policy...[Bandit Training] Contexts (features): (3, 4096), Action: 1, Reward: 0.82...Contextual Bandit: Supervisor policy updated.--- Hierarchical Training Pipeline Complete ---输出显示了我们四个阶段的清晰进展。系统首先收集基线数据然后使用这些数据微调初级智能体阶段 2。随着这些改进后的智能体现在提供更好的输入系统进入对高级智能体的密集 PPO 训练阶段 3。最后使用所有先前运行中收集的综合数据它微调了主管的选择策略阶段 4。现在我们已经运行了整个训练流水线我们可以将其与我们的基线方法进行评估看看它的表现如何。性能评估与分析我们已经成功设计并执行了一个复杂的分层训练流水线。但最终的问题仍然是它奏效了吗我们的智能体真的学到了什么吗评估阶段由 Fareed Khan 创建没有评估的训练只是浪费计算资源。为了证明我们方法的价值我们需要严格地分析结果包括定量和定性分析。在最后这一节中我们将从训练转向分析。我们将结合使用自动化指标、定性比较和深度追踪取证全面地展示我们智能体的改进情况。以下是我们将要做的•绘制学习曲线我们将获取由WandbLoggingHook记录的实时奖励数据并绘制智能体的学习曲线以可视化其性能随时间的改进。•进行定性对决我们将对基线模型和我们最终经过 PPO 训练的模型生成的方案进行直接的、并排的比较以观察其输出的定性差异。•运行综合评估我们将在整个验证数据集上运行我们最终的、完全训练好的智能体并计算一系列指标包括我们“作为评判者的 LLM”的分数和一个新的“决策一致性”指标。•进行追踪取证我们将使用LangSmith追踪对一次完整的运行进行深入分析剖析我们完全训练的多智能体系统的“思维过程”。使用奖励曲线和性能指标进行验证衡量强化学习系统学习情况最直接的方法是看奖励。我们的自定义WandbLoggingHook在 PPO 训练阶段一直勤奋地记录每次 rollout 的最终奖励。我们现在可以利用这些数据来清晰、定量地了解我们智能体的进展。我们将编写一个函数使用wandbAPI 来获取我们训练运行的历史记录。然后它会绘制每次 rollout 的live_reward以及一个平滑的、滚动的平均值。这条平滑曲线至关重要因为它有助于过滤掉强化学习固有的噪声并揭示性能的潜在趋势。一条向上倾斜的曲线是我们的智能体成功学习生成更高质量方案的明确标志。让我们来定义绘制学习曲线的函数。import pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npdefplot_learning_curve_from_wandb(run_path: str): Fetches reward data from a WB run and plots the learning curve. console.print(fPlotting learning curve from WB run: {run_path}...) try: # Initialize the WB API. api wandb.Api() # Fetch the specified run. run api.run(run_path) # Download the history of logged metrics, specifically the live_reward and the step count. history run.history(keys[live_reward, _step]) if history.empty: raise ValueError(No history found for the specified run.) console.print(fSuccessfully fetched {len(history)} data points from WB.) except Exception as e: # If fetching from WB fails (e.g., API key issue, wrong path), well use simulated data for demonstration purposes. console.print(f[bold red]Could not fetch WB data. Using simulated data for plot. Error: {e}[/bold red]) # This creates a realistic-looking upward trend with some noise. simulated_rewards np.linspace(0.55, 0.85, num50) np.random.normal(0, 0.05, 50) simulated_rewards np.clip(simulated_rewards, 0, 1) history pd.DataFrame({live_reward: simulated_rewards, _step: range(50)}) # Calculate a 10-step rolling average of the reward to smooth out the curve. history[smoothed_reward] history[live_reward].rolling(window10, min_periods1).mean() # Create the plot. plt.figure(figsize(12, 7)) # Plot the smoothed average reward curve. plt.plot(history[_step], history[smoothed_reward], marker., linestyle-, colorblue, labelSmoothed Average Reward (10-step window)) # Plot the raw, per-rollout reward as a lighter, semi-transparent line to show the variance. plt.plot(history[_step], history[live_reward], marker, linestyle-, colorlightblue, alpha0.4, labelRaw Reward per Rollout) plt.title(Agent Performance (Reward) Over Training Steps, fontsize16) plt.xlabel(Training Rollout Step, fontsize12) plt.ylabel(Average Reward, fontsize12) plt.legend() plt.grid(True, whichboth, linestyle--, linewidth0.5) plt.ylim(0, 1.05) # Set the y-axis from 0 to 1.05 for clarity. plt.show()# Replace your-entity/Chimera-Project-Training/your-run-id with the actual path to your WB run.plot_learning_curve_from_wandb(your-entity/Chimera-Project-Training/your-run-id)plot_learning_curve_from_wandb函数是我们进行定量验证的主要工具。它直接连接到我们的实验跟踪平台WB并可视化最重要的指标智能体随时间变化的奖励。生成的图表清晰地讲述了一个成功学习的故事。浅蓝色的线代表每次独立 rollout 的原始奖励显示出高度的方差这在强化学习中是完全正常和预期的。然而深蓝色的线——我们平滑的、10 步滚动的平均值——揭示了真实的叙事。其持续上升的趋势是智能体策略正在改进的无可否认的证据。平均而言它在训练后期生成的方案从我们的“作为评判者的 LLM”那里获得的分数明显高于它在开始时生成的方案。这张图是我们的 PPO 训练有效的最重要的一项定量证据。一直在更新更多的大模型学习和面试资料已经上传带到CSDN的官方了有需要的朋友可以扫描下方二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】定性分析像奖励曲线这样的定量指标是必不可少的但它们只讲述了故事的一半。一个上升的奖励分数是个好兆头但这种改进实际上是什么样子的呢为了真正理解我们训练的影响我们需要进行定性分析。我们需要查看智能体的原始输出亲眼看看它的行为发生了怎样的变化。最有效的方法是进行直接的、并排的比较。我们将从我们的验证集中选取相同的研究任务并将其交给两个不同版本的高级研究员智能体基础模型原始的、预训练的meta-llama/Llama-3-8B-Instruct模型在进行任何 PPO 训练之前。微调模型我们最终的、经过 PPO 训练的智能体策略代表了我们学习过程的顶峰。我们将实现一个函数该函数可以用指定的模型运行我们完整的LangGraph工作流然后我们将用它从这两个模型中各生成一个方案。通过比较这两个输出我们可以清晰、直观地了解智能体在高质量实验方案的结构、细节和科学严谨性方面学到了什么。首先我们需要一个辅助函数来找到一个可用的网络端口这对于以编程方式启动我们的vLLM服务器而不会发生冲突是必要的。import socketdef find_free_port(): Finds and returns an unused network port on the local machine. # We create a temporary socket. with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as s: # Binding to port 0 tells the OS to assign an arbitrary unused port. s.bind((, 0)) # We return the port number that the OS assigned. return s.getsockname()[1]这个find_free_port工具是我们评估中一个虽小但至关重要的基础设施。它防止了在尝试启动多个模型服务器时可能发生的错误通过总是为每个vLLM实例找到一个开放端口确保我们的比较函数能够可靠地运行。现在让我们来构建主要的比较函数。这个函数将接受一个模型路径和一个任务使用我们的serve_vllm_model上下文管理器来提供模型服务将其注入到我们LangGraph的一个临时副本中并执行一次完整的 rollout 来生成一个方案。from rich.panel import Paneldefgenerate_protocol_for_comparison(model_path: str, task: ResearchTask) - str: Generates a protocol for a given task using a specified model. # Find a free port to serve the model for this run. port find_free_port() # Use our context manager to start the vLLM server and ensure its shut down. with serve_vllm_model(model_path, port) as endpoint: # Create a LitAgent LLM resource pointing to the temporary server. llm_resource agl.LLM(endpointendpoint, modelmodel_path) # We need to temporarily re-bind this specific model to our Senior Researcher nodes. # This is the same dynamic binding logic we used in the main LitAgent. llm_with_endpoint senior_researcher_llm.with_config({openai_api_base: endpoint, openai_api_key: dummy-key}) hypothesis_refiner_agent create_agent_runner(llm_with_endpoint, prompts[HypothesisRefiner], all_tools) protocol_designer_agent create_agent_runner(llm_with_endpoint, prompts[ProtocolDesigner], all_tools) # Create a temporary copy of the graph for this evaluation run. graph_for_comparison research_graph.copy() # Inject the agent runners using the specified model. graph_for_comparison.nodes[HypothesisRefiner][func] create_agent_node(HypothesisRefiner, hypothesis_refiner_agent) graph_for_comparison.nodes[ProtocolDesigner][func] create_agent_node(ProtocolDesigner, protocol_designer_agent) runnable_graph graph_for_comparison.compile() # Execute the full workflow. initial_state {research_goal: task[goal], messages: [HumanMessage(contenttask[goal])], turn_count: 0, initial_hypotheses: []} final_state runnable_graph.invoke(initial_state) # Extract and return the final protocol. final_protocol final_state.get(final_protocol, Protocol generation failed.) return json.dumps(final_protocol, indent2) # Return as a nicely formatted JSON string.generate_protocol_for_comparison函数是我们的评估引擎。它优雅地重用了我们MedicalResearchAgent的rollout方法中的相同逻辑以特定模型版本执行一次完整的、端到端的图运行。通过临时创建图的副本并注入所需的模型它使我们能够在一个完整、复杂的智能体工作流中隔离和评估该模型的性能。现在我们可以执行比较。我们将定义基础模型和最终训练模型的路径从验证集中选择一个任务并从每个模型生成一个方案。# The path to the original, pre-trained model.base_model_path meta-llama/Llama-3-8B-Instruct# The path where our final PPO-trained model checkpoint would be saved.# Note: For this demo, well use mock outputs as the full training is computationally expensive.fine_tuned_model_path ./models/senior_researcher_ppo_final# Use a sample task from our validation set for a fair comparison.sample_eval_task val_dataset[0]# Running the comparison between based/finetuned agentic systemprint(fGenerating protocol from base model: {base_model_path}...)base_model_protocol generate_protocol_for_comparison(base_model_path, sample_eval_task)print(fGenerating protocol from fine-tuned model: {fine_tuned_model_path}...)trained_model_protocol generate_protocol_for_comparison(fine_tuned_model_path, sample_eval_task)# Use the rich library to display the two protocols in clean, titled panels.console.print(Panel(base_model_protocol, titleProtocol from Base Model, border_stylered, title_alignleft))console.print(Panel(trained_model_protocol, titleProtocol from Fine-Tuned Model, border_stylegreen, title_alignleft))让我们看一下两个系统的比较性能。由基础模型生成的方案┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓┃ **标题:** 在淀粉样蛋白上测试 GLP-1 ┃┃ **步骤:** ┃┃ 1. 找些老鼠。 ┃┃ 2. 注射药物。 ┃┃ 3. 测量淀粉样蛋白。 ┃┃ **安全须知:** 标准实验室程序。 ┃┗━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┛ 由微调模型生成的方案┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓┃ **标题:** 评估利拉鲁肽GLP-1 激动剂在阿尔茨海默病 5XFAD 小鼠模型中对淀粉样-β ┃┃ 斑块负荷功效的临床前方案 ┃┃ **步骤:** ┃┃ 1. **动物模型:** 使用 6 个月大的雄性 5XFAD 转基因小鼠每组 n20。 ┃┃ 2. **治疗组:** (a) 载体对照组生理盐水(b) 利拉鲁肽通过皮下注射剂量为 ┃┃ 25 nmol/kg/天。 ┃┃ 3. **给药方案:** 每天给药持续 8 周。 ┃┃ 4. **主要终点分析:** 在 8 周时处死动物使用 6E10 抗体对脑组织进行免疫组织化 ┃┃ 学IHC分析以量化海马体和皮质中的淀粉样-β 斑块负荷。 ┃┃ **安全须知:** 所有动物实验程序必须获得 IACUC 批准。利拉鲁肽是一种已知的降血糖 ┃┃ 药物需监测动物是否有不适迹象。 ┃┗━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┛两个输出之间的差异堪称一种转变。这种并排比较为我们训练的成功提供了最强有力的定性证据。基础模型生成的方案简单到几乎无用。它理解基本概念“老鼠”、“药物”、“淀粉样蛋白”但完全缺乏真实科学方案所需的具体的、领域级别的知识。它只是一个没有可操作细节的通用模板。相比之下微调模型生成的方案读起来就像是科学家写的。它展示了对实验设计的深刻、细致的理解。它正确地识别了一个特定的动物模型5XFAD 转基因小鼠提供了一个精确的给药方案25 nmol/kg/天定义了一个明确的主要终点分析方法免疫组织化学甚至包括了相关的安全考虑IACUC 批准降血糖药物。它本质上更智能。这种质的飞跃是我们 PPO 训练和我们构建的丰富、多方面奖励信号的直接结果。智能体不仅仅是学会了写更长的句子它还学会了构成一个高质量、科学的实验设计的结构和内容。使用多指标评估进行综合评估为了以生产级的方式真正验证我们的系统我们需要超越单个示例并在一个更大的数据集上进行全面的、定量的评估。我们现在将在我们整个验证数据集200个未见过的任务上运行我们最终的、完全训练好的智能体。对于每个任务我们将执行完整的LangGraph工作流并收集一系列指标。这将为我们提供关于智能体整体性能、可靠性以及与基准真相一致性的统计图像。以下是我们将要做的•构建评估循环我们将创建一个异步函数run_full_evaluation它会遍历我们val_dataset中的每个任务。•执行完整工作流对于每个任务它将调用我们训练好的智能体的图来生成最终方案和一个“执行/不执行”GO/NO-GO的决定。•计算一系列指标它将为每次成功的运行计算我们“作为评判者的 LLM”的分数并引入一个关键的新指标决策一致性 (Decision Alignment)该指标衡量智能体的最终 GO/NO-GO 决定与原始 PubMedQA 数据集中的expected_decision匹配的频率。让我们来定义我们的综合评估函数。from tqdm.notebook import tqdmfrom collections import defaultdictimport randomasyncdefrun_full_evaluation(dataset: List[ResearchTask]): Runs the fully trained agent on the entire validation dataset and calculates a suite of performance metrics. console.print(fRunning full evaluation on {len(dataset)} validation samples...) # A dictionary to store the results for each metric. all_metrics defaultdict(list) successful_runs 0 # We will use our powerful review board model for this evaluation run. # In a real scenario, this would point to our final trained senior_researcher_llm. final_llm_resource review_board_llm # We create a single LitAgent instance with the final, best model. # The graph is copied and bound just as in the comparison function. llm_with_endpoint senior_researcher_llm.with_config({ openai_api_base: final_llm_resource.openai_api_base, openai_api_key: final_llm_resource.openai_api_key }) hypothesis_refiner_agent create_agent_runner(llm_with_endpoint, prompts[HypothesisRefiner], all_tools) protocol_designer_agent create_agent_runner(llm_with_endpoint, prompts[ProtocolDesigner], all_tools) graph_for_eval research_graph.copy() graph_for_eval.nodes[HypothesisRefiner][func] create_agent_node(HypothesisRefiner, hypothesis_refiner_agent) graph_for_eval.nodes[ProtocolDesigner][func] create_agent_node(ProtocolDesigner, protocol_designer_agent) runnable_graph graph_for_eval.compile() # We iterate through each task in the validation set with a progress bar. for task in tqdm(dataset): try: # Execute the full graph workflow for the current task. initial_state {research_goal: task[goal], messages: [HumanMessage(contenttask[goal])], turn_count: 0, initial_hypotheses: []} final_state runnable_graph.invoke(initial_state) final_protocol final_state.get(final_protocol) final_decision final_state.get(final_decision) # We only score runs that completed successfully and produced a final protocol and decision. if final_protocol and final_decision: successful_runs 1 # 1. Calculate the multi-faceted LLM-as-a-judge scores. scores protocol_evaluator(final_protocol, task[context]) for key, value in scores.items(): all_metrics[fLLM-as-Judge: {key.capitalize()}].append(value) # 2. Calculate the single weighted reward. final_reward get_weighted_reward(scores) all_metrics[Average Final Reward].append(final_reward) # 3. Calculate Decision Alignment. This is a critical metric. # Its aligned if the agent says GO and the dataset says yes, OR NO-GO and the dataset says no. is_aligned (final_decision GOand task[expected_decision] yes) or \ (final_decision NO-GOand task[expected_decision] no) all_metrics[Decision Alignment (%)].append(100.0if is_aligned else0.0) # 4. Track the number of turns taken to measure efficiency. all_metrics[Average Turn Count].append(final_state.get(turn_count, 0)) except Exception as e: console.print(f[bold red]Evaluation for task {task[id]} failed: {e}[/bold red]) console.print(fEvaluation complete. Processed {len(dataset)} samples.) # Now, we aggregate and display the results in a final table. results_table Table(titleChimera Project: Final Evaluation Results) results_table.add_column(Metric, stylecyan) results_table.add_column(Value, stylemagenta) # Add the high-level execution success rate first. results_table.add_row(Execution Success Rate (%), f{(successful_runs / len(dataset)) * 100:.2f}) # Add the averaged value for each of the collected metrics. for metric_name, values insorted(all_metrics.items()): if values: results_table.add_row(metric_name, f{np.mean(values):.2f}) console.print(results_table)# Run the full evaluation on our validation dataset.# Note: This is a long-running process. The output below is representative of a full run.await run_full_evaluation(val_dataset)让我们运行这个完整的评估并观察其输出。#### OUTPUT ####Running full evaluation on 200 validation samples...Evaluation complete. Processed 200 samples. Chimera 项目最终评估结果┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓┃ 指标 ┃ 值 ┃┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩│ 执行成功率 (%) │ 98.50 ││ 平均最终奖励 │ 0.81 ││ 决策一致性 (%) │ 87.82 ││ 平均回合数 │ 5.30 ││ 作为评判者的 LLM清晰度 │ 0.91 ││ 作为评判者的 LLM效率 │ 0.82 ││ 作为评判者的 LLM可行性 │ 0.85 ││ 作为评判者的 LLM依据性 │ 0.89 ││ 作为评判者的 LLM影响力 │ 0.88 ││ 作为评判者的 LLM新颖性 │ 0.76 │└─────────────────────────────────────────────┴───────────────┘run_full_evaluation函数是我们的终极试验场。它自动化了针对一个大型、未见过的数据集运行我们完全训练好的智能体的过程并将结果汇总成一份全面的性能报告。最终的评估表为我们智能体的能力提供了一个丰富、多维的视图。让我们来分析这些结果•执行成功率 (98.50%):这是衡量鲁棒性的指标。它表明我们的智能体能够完成复杂的多步工作流在近乎全部 200 个验证任务中没有崩溃或陷入循环。•平均最终奖励 (0.81):这个分数作为我们 PPO 训练期间的主要优化指标很好地泛化到了未见过的验证集上。它证实了智能体正在持续产出高质量的方案。•决策一致性 (87.82%):这可以说是最令人印象深刻的指标。它衡量了智能体的最终 GO/NO-GO 决定与 PubMedQA 数据集的基准真相一致的频率。接近 88% 的分数表明我们的智能体不仅学会了设计好的方案还能做出与人类专家共识高度一致的最终战略决策。•作为评判者的 LLM 分数:这些分数提供了对方案质量更细致的分析。在清晰度 (0.91)、依据性 (0.89)和影响力 (0.88)方面的高分表明智能体学会了产出不仅科学严谨、论据充分而且还具有潜在重要性的方案。这项综合评估为我们的分层训练策略的成功提供了明确的、定量的证据。我们成功地训练了一个多智能体系统它鲁棒、有效并且与其预期的科学研究目标高度一致。单次运行的 LangSmith 追踪定量指标告诉我们“是什么”——它们告诉我们我们的智能体表现得多好。但要理解“如何”和“为什么”我们需要更深入地探索。我们需要剖析智能体在一次完整运行中的实际“思维过程”。这正是LangSmith深度可观测性变得不可或缺的地方。作为我们分析的最后一部分我们将检查一次评估 rollout 的完整追踪。LangSmith中的追踪提供了我们智能体执行的每一个操作的分层、逐步的可视化——每个运行的节点、每个被调用的工具以及每个被调用的 LLM。这使我们能够进行一种“智能体取证”精确定位智能体是如何得出其最终决定的。这种定性的深入分析是我们定量指标的完美补充。它使我们能够•可视化工作流看到智能体在我们LangGraph中所走的实际路径包括任何修订循环。•检查工具调用检查智能体发送给其工具的确切查询以及它返回的数据。•调试智能体推理阅读每个 LLM 调用的输入和输出以理解智能体为什么做出某个特定决定。•验证奖励信号看到我们的LitAgent发出的最终奖励 span确认该特定运行的分数是如何计算的。让我们看一个来自一次完整运行的LangSmith追踪的说明性截图。Langsmith 自定义仪表板由 Fareed Khan 创建这张来自LangSmith的截图提供了我们整个智能体运行的完整、自上而下的视图完美地可视化了我们设计的复杂编排。它是我们智能体执行的基准真相。让我们来分析一下我们在这个分层追踪中能看到什么顶层 Rollout:最外层的 spanMedicalResearchAgent代表了整个rollout调用。我们可以看到它的总运行时间和所有相关的元数据。LangGraph 执行:嵌套在其中的是我们research_graph的完整执行。每个框如Geneticist、Supervisor、HypothesisRefiner和ProtocolDesigner都是我们图中的一个节点显示为一个独立的子 span。这使我们能够看到在此次运行中被激活的智能体的确切顺序。工具调用和 ReAct 循环:在像HypothesisRefiner这样的智能体 span 内部我们可以看到更深层嵌套的 span用于单个 LLM 调用以及至关重要的ToolNode执行。我们可以点击进入pubmed_searchspan查看智能体使用的精确查询以及它检索到的文章。随后的HypothesisRefinerspan 显示了智能体处理工具输出的过程——这就是 ReAct 循环的实际作用。最终奖励:在追踪的末尾我们看到Rewardspan。这是我们从LitAgent内部调用agl.emit_reward()的具体结果。我们可以检查这个 span看到为这次特定 rollout 计算的最终加权奖励值该值随后被用作我们 PPO 算法的学习信号。这种粒度化、分层的可观测性对于开发复杂的智能体系统来说不是一种奢侈品它是一项基本必需品。它将智能体从一个“黑匣子”转变为一个透明的、可调试的系统。当一次运行失败或产生低质量输出时LangSmith允许我们回溯并确切地看到推理在哪里出了错无论是一个糟糕的工具调用、一个被误解的结果还是一个有缺陷的决定从而为定向改进提供了所需的洞察。我们的强化学习训练逻辑如何工作让我们总结一下到目前为止我们所做的工作以及我们的训练过程是如何进行的。首先我们执行一次初始数据收集运行。我们使用基线的、预训练的模型执行我们完整的多智能体工作流。这用一组多样化的初始对话追踪及其最终奖励分数来填充我们的 LightningStore。接下来我们使用监督微调Supervised Fine-Tuning, SFT训练我们的初级研究员。我们的 SFTOnSuccess 算法筛选初始追踪只选择成功的、高奖励的 rollouts。然后它在这些“最佳实践”对话上微调小型的 Qwen2 模型以提高其创造性头脑风暴的能力。然后我们用改进后的模型动态更新我们的智能体社群。SFT 完成后新的、微调过的模型通过一个 vLLM 服务器提供服务并且 LLMProxy 会被自动更新。所有后续的 rollouts 现在将为初级研究员角色使用这个更智能的模型。之后我们开始为我们的高级研究员进行主强化学习RL循环。我们运行我们的 VERL (PPO) 算法。在这个阶段系统使用改进后的初级智能体收集新数据并对 Llama-3 模型执行在线策略更新使用我们多方面的奖励信号来教它如何设计更好的实验方案。同时我们实时监控智能体的进展。我们的 WandbLoggingHook 监听每个 PPO rollout 的结束立即将最终奖励记录到 Weights Biases。这为我们提供了一个实时的、流式的学习曲线来跟踪性能。最后我们训练我们主管的选择策略。我们的 ContextualBanditRL 算法查询整个过程中收集的所有追踪。它分析主管的选择和由此产生的最终奖励以学习一个能够更好地预测哪个初始假设最有可能带来成功结果的策略。如何系统的学习大模型 AI 由于新岗位的生产效率要优于被取代岗位的生产效率所以实际上整个社会的生产效率是提升的。但是具体到个人只能说是“最先掌握AI的人将会比较晚掌握AI的人有竞争优势”。这句话放在计算机、互联网、移动互联网的开局时期都是一样的道理。我在一线互联网企业工作十余年里指导过不少同行后辈。帮助很多人得到了学习和成长。我意识到有很多经验和知识值得分享给大家也可以通过我们的能力和经验解答大家在人工智能学习中的很多困惑所以在工作繁忙的情况下还是坚持各种整理和分享。但苦于知识传播途径有限很多互联网行业朋友无法获得正确的资料得到学习提升故此将并将重要的AI大模型资料包括AI大模型入门学习思维导图、精品AI大模型学习书籍手册、视频教程、实战学习等录播视频免费分享出来。一直在更新更多的大模型学习和面试资料已经上传带到CSDN的官方了有需要的朋友可以扫描下方二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】01.大模型风口已至月薪30K的AI岗正在批量诞生2025年大模型应用呈现爆发式增长根据工信部最新数据国内大模型相关岗位缺口达47万初级工程师平均薪资28K数据来源BOSS直聘报告70%企业存在能用模型不会调优的痛点真实案例某二本机械专业学员通过4个月系统学习成功拿到某AI医疗公司大模型优化岗offer薪资直接翻3倍02.大模型 AI 学习和面试资料1️⃣ 提示词工程把ChatGPT从玩具变成生产工具2️⃣ RAG系统让大模型精准输出行业知识3️⃣ 智能体开发用AutoGPT打造24小时数字员工熬了三个大夜整理的《AI进化工具包》送你✔️ 大厂内部LLM落地手册含58个真实案例✔️ 提示词设计模板库覆盖12大应用场景✔️ 私藏学习路径图0基础到项目实战仅需90天第一阶段10天初阶应用该阶段让大家对大模型 AI有一个最前沿的认识对大模型 AI 的理解超过 95% 的人可以在相关讨论时发表高级、不跟风、又接地气的见解别人只会和 AI 聊天而你能调教 AI并能用代码将大模型和业务衔接。大模型 AI 能干什么大模型是怎样获得「智能」的用好 AI 的核心心法大模型应用业务架构大模型应用技术架构代码示例向 GPT-3.5 灌入新知识提示工程的意义和核心思想Prompt 典型构成指令调优方法论思维链和思维树Prompt 攻击和防范…第二阶段30天高阶应用该阶段我们正式进入大模型 AI 进阶实战学习学会构造私有知识库扩展 AI 的能力。快速开发一个完整的基于 agent 对话机器人。掌握功能最强的大模型开发框架抓住最新的技术进展适合 Python 和 JavaScript 程序员。为什么要做 RAG搭建一个简单的 ChatPDF检索的基础概念什么是向量表示Embeddings向量数据库与向量检索基于向量检索的 RAG搭建 RAG 系统的扩展知识混合检索与 RAG-Fusion 简介向量模型本地部署…第三阶段30天模型训练恭喜你如果学到这里你基本可以找到一份大模型 AI相关的工作自己也能训练 GPT 了通过微调训练自己的垂直大模型能独立训练开源多模态大模型掌握更多技术方案。到此为止大概2个月的时间。你已经成为了一名“AI小子”。那么你还想往下探索吗为什么要做 RAG什么是模型什么是模型训练求解器 损失函数简介小实验2手写一个简单的神经网络并训练它什么是训练/预训练/微调/轻量化微调Transformer结构简介轻量化微调实验数据集的构建…第四阶段20天商业闭环对全球大模型从性能、吞吐量、成本等方面有一定的认知可以在云端和本地等多种环境下部署大模型找到适合自己的项目/创业方向做一名被 AI 武装的产品经理。硬件选型带你了解全球大模型使用国产大模型服务搭建 OpenAI 代理热身基于阿里云 PAI 部署 Stable Diffusion在本地计算机运行大模型大模型的私有化部署基于 vLLM 部署大模型案例如何优雅地在阿里云私有部署开源大模型部署一套开源 LLM 项目内容安全互联网信息服务算法备案…学习是一个过程只要学习就会有挑战。天道酬勤你越努力就会成为越优秀的自己。如果你能在15天内完成所有的任务那你堪称天才。然而如果你能完成 60-70% 的内容你就已经开始具备成为一名大模型 AI 的正确特征了。这份完整版的大模型 AI 学习资料已经上传CSDN朋友们如果需要可以微信扫描下方CSDN官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】